|
2015 Burkinabè general election
General elections were held in Burkina Faso on 29 November 2015. These were the first national elections in the country since the 2014 Burkinabé uprising and the departure of President Blaise Compaoré, who had ruled Burkina Faso for 27 years. Compaoré's political party, the Congress for Democracy and Progress, was banned from presenting a presidential candidate in the presidential elections but was still able to participate in the parliamentary election. The presidential election was won by Roch Marc Christian Kaboré of the People's Movement for Progress, who received 53% of the vote in the first round, avoiding the need for a second round. Kaboré took office on 29 December, becoming only the second civilian president since the country gained independence from France in 1960 and the first civilian to hold the post in 49 years. Background2014 uprisingFollowing an amendment in 2000, the constitution limits presidents to two terms of five years. However, the restrictions were not applied retrospectively, allowing President Blaise Compaoré, who had been in office since 1987, to run for a further two terms; accordingly, he was re-elected in 2005 and 2010.[1] On 30 October 2014 the National Assembly was scheduled to vote on a constitutional amendment that would scrap term limits. However, the vote sparked protests, with the National Assembly building, Ouagadougou City Hall and the Congress for Democracy and Progress headquarters set on fire. As a result of the protests, the vote was suspended.[1] Protests were also reported in other cities, including the second largest city Bobo Dioulasso. Compaoré subsequently announced that he would withdraw the constitutional amendment.[2] On 31 October, Compaoré resigned and suggested an election should be held within 90 days.[3] Armed Forces Chief of Staff General Honoré Traoré first assumed the role of acting head of state. However, many protesters criticised the new transition of power because of Traoré's ties to Compaoré. Some protesters have called for the election of Kouamé Lougué.[3] After a brief power struggle, the armed forces asserted that Yacouba Isaac Zida had their unanimous backing to be the interim head of state, although some protests continued against having a military-led interim administration. Presidential candidatesThe transitional charter barred any ministers in the transitional government from running for the presidency.[4] The following politicians declared their intent to stand as presidential candidates, although some were barred from running:
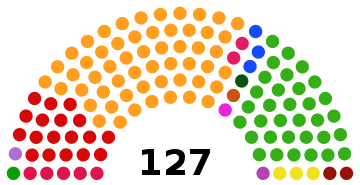
Electoral code and controversyIn April 2015 the interim legislature passed an electoral code banning any MPs who supported the constitutional amendment to scrap term limits from contesting the elections.[11][12] The reform of the electoral code was adopted by the transitional parliament on 7 April and signed by President Kafando on 10 April. In protest, the former ruling CDP and its allies announced on 10 April 2015 that they were suspending participation in the National Transition Council and the National Commission for Reconciliation and Reforms, saying the new electoral code was a means of political exclusion.[12] On 13 July 2015, the ECOWAS Court of Justice ruled against the exclusionary law. According to the court, preventing people from contesting the elections on the basis of a political stance was "a violation of their fundamental human rights".[13] On 16 July 2015 President Kafando confirmed that Burkina Faso would apply ECOWAS's judgment.[14] However, on the same day the transitional government charged Blaise Compaoré with "high treason" over his bid to change the constitution and run for a third term. In addition to these charges against Compaoré, the transitional parliament brought murder and assault charges against all government officials who approved of his bid to stay on.[15] The sudden charges were criticized by some, as they were perceived as a new manoeuvre from the transitional government to exclude all serious candidates from running in the upcoming elections. It also reasserted the suspicions of partiality and instrumentalisation that surround the transitional government. Compaoré supporters appealed to the Constitutional Council to annul the charges.[16] On 10 August, the court ruled that it lacked the authority to decide whether the charges should be annulled.[17] 22 people submitted applications to stand as presidential candidates by the deadline at midnight on 21 August 2015. The list included politicians who had served under Compaoré, such as Djibril Bassolé, as well as politicians who had opposed him, such as Bénéwendé Sankara and Zéphirin Diabré.[18] Despite the ECOWAS ruling against the exclusionary law, the Constitutional Council ruled on 25 August that the law had never been overturned by the authorities in Burkina Faso and therefore remained in effect. Accordingly, it barred 42 prospective candidates who had supported changing the constitution from standing as parliamentary candidates, including CDP leader Eddie Komboïgo and ADF-RDA leader Gilbert Noel Ouedraogo.[19][20] Outraged, the CDP vowed civil disobedience and potentially an electoral boycott, arguing that the ruling was illegal and unconstitutional, that it denied the rights of citizens to participate in the political process and ignored the ECOWAS ruling. Parties which had supported Compaoré promptly appealed to the Authority of ECOWAS Heads of State and Government.[21] On 29 August 2015, the Constitutional Council announced that 16 of the 22 prospective candidates would be allowed to run. As with the parliamentary election, CDP leader Eddie Komboïgo and ADF-RDA leader Gilbert Noel Ouedraogo were barred from running. All of the other candidates were allowed to run, except for four independent candidates who failed to pay the necessary deposit. Djibril Bassolé, who was Compaoré's last foreign minister, was cleared to stand.[22][23] Komboïgo condemned the court's ruling, saying that it was politically motivated.[24] Three candidates argued that Djibril Bassolé and Yacouba Ouedraogo, who were both serving in the government when Compaoré was ousted in October 2014, should also be excluded because they were present at a government meeting to prepare legislation that would have scrapped presidential term limits. The Constitutional Council accepted this argument, and on 10 September 2015 it struck Bassolé and Ouedraogo from the list of approved candidates. Of the 14 remaining candidates, Roch Marc Christian Kabore and Zéphirin Diabré, both of whom served in the government under Compaoré but later broke with him and went into opposition, were viewed as the leading contenders.[25] September 2015 coupOn 16 September 2015, the Regiment of Presidential Security (RSP), the presidential guard closely linked to Compaoré, detained President Kafando and Prime Minister Zida, two days after the reforms commission had recommended dissolving the RSP. The coup leaders announced on 17 September that they were dismissing Kafando, dissolving the government and the transitional legislature, and setting up a new transitional body, the National Council for Democracy (CND), to lead the country to "inclusive and peaceful elections". In their proclamation of the CND, they denounced the transitional authorities for their allegedly undemocratic electoral law and for ignoring the recommendations of ECOWAS to scrap the exclusionary law.[26] General Gilbert Diendéré was appointed as chairman of the council.[27] Later in the day, Diendéré said that Compaoré had nothing to do with the coup and that the coup was supported by the rest of the army. He called for calm "so that we can continue on the path to inclusive and democratic elections" and appealed to the international community: "We know a coup is never accepted by the international community, but we ask it to understand the purpose of our action. We are committed to dialogue and accept certain principles of the international community." He stressed that he had no interest in politics and was only getting involved due to the "special situation", and he said that power would be returned to civilians "as soon as conditions are there".[27] In other comments, he said that presidential and parliamentary elections would be held on a new timetable, which would be determined through consultations with "the concerned actors, notably the political parties and civil society organisations". He also promised that the exclusionary electoral law would be changed so that all political forces could participate.[28] Two regional leaders—Macky Sall, the President of Senegal and Chairman of ECOWAS, and Boni Yayi, the President of Benin—travelled to Ouagadougou on 18 September to hold talks with Diendéré, aiming to restore the transitional government.[29] On 20 September, a draft agreement was announced that would involve allowing the previously excluded candidates to participate in the election. It also granted amnesty to those who participated in the coup and required the release of those who were detained by the CND. It also allowed a delay in the holding of the election, but required that it be held by 22 November.[30] The two sides appeared to still disagree about who would lead the transition: the draft agreement called for restoring Kafando as president, but the CND insisted that Diendéré should continue in his post for the remainder of the transitional period.[31] The CND never clearly established its authority beyond Ouagadougou, and on 21 September army leaders announced that soldiers from the regular army were marching towards the capital to put an end to the coup.[32] Facing the prospect of a confrontation with the regular army as well as ongoing street protests by opponents of the coup, who felt that the proposed terms offered too many concessions to the coup leaders, Diendéré said that the CND would abide by the draft agreement's provision for the return of civilian rule.[33] Kafando was reinstalled as president at a ceremony on 23 September in the presence of ECOWAS leaders. Isaac Zida also returned to his post as Prime Minister. Zida said that he foresaw a delay of "several weeks" in the holding of the election. For his part, Diendéré said that the coup was a mistake and that "we knew the people were not in favour of it. That is why we have given up."[34] On 25 September the RSB was disbanded by government decree. On 26 September the assets of Diendéré and others associated with the coup, as well as the assets of four political parties, including the CDP, were frozen by the state prosecutor.[35] Djibril Bassolé and Eddie Komboïgo, who were barred from standing as presidential candidates, both had their assets frozen.[36] Bassolé was arrested on 29 September for allegedly supporting the coup.[37] Electoral systemThe President was elected using the two-round system, with a run-off election due to be held 15 days after the election results were declared if no candidate received over 50% of the vote in the first round. CampaignIt was reported on 13 October that the election would be held on 29 November 2015.[38] Later in the month, the CDP stated that, with its own candidate barred from running, it planned to support another candidate in the election. It also said that it would replace its parliamentary candidates who had been barred from running.[39] The official campaigning period began on 8 November, with 14 presidential candidates running. Kabore launched his campaign in Bobo-Dioulasso, with 30,000 supporters in attendance, while Diabre launched his campaign in Fada N'Gourma and Sankara in Solenzo.[40] The campaign heavily favored wealthy candidates and did not provide opportunities for parties with fewer resources to build grassroots campaigns.[41] Some candidates had sufficient wealth to employ helicopters to ferry them between campaign rallies and rally support from the country's predominately rural population. ResultsPartial results released on 30 November, reflecting votes from 253 out of 368 communes, showed Kaboré with a strong lead over Diabré, 54.27% to 29.16%.[42] The electoral commission announced on 1 December that Kaboré had won the election in the first round with 53.5% of the vote against 29.7% for Diabré. Turnout was placed at about 60%.[41][43] Results for the parliamentary election were announced on 2 December 2015, showing that Kaboré's party, the MPP, placed first with 55 out of 127 seats, but fell short of a majority. Diabré's party, the UPC, won 33 seats, and the CDP won 18.[44] Final official results from the Constitutional Council were announced on 15 December 2015, confirming that Kaboré won the election with 53% of the vote.[45] He was sworn in as president on 29 December 2015.[46] The National Assembly elected Salif Diallo, a leading member of the MPP, as President of the National Assembly on 30 December. He received 78 votes from the 127 deputies.[47] President
National Assembly
ReactionsThe head of the electoral commission, Barthelemy Kere, said that "this election went off in calm and serenity, which shows the maturity of the people of Burkina Faso."[43] Zephirin Diabre, the runner-up in the vote, came to President-elect Roch Marc Christian Kabore's campaign headquarters as Kabore's supporters celebrated the win to congratulate him, Al Jazeera reported.[48] Foreign governments also extended congratulations to Kabore, including those of Ghana[49] and the United States.[50] References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||