|
Aromatic amino acid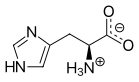 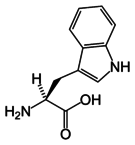  An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring.  Among the 20 standard amino acids, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine, are classified as aromatic. Properties and functionOptical propertiesAromatic amino acids, excepting histidine, absorb ultraviolet light above and beyond 250 nm and will fluoresce under these conditions. This characteristic is used in quantitative analysis, notably in determining the concentrations of these amino acids in solution.[1][2] Most proteins absorb at 280 nm due to the presence of tyrosine and tryptophan. Of the aromatic amino acids, tryptophan has the highest extinction coefficient; its absorption maximum occurs at 280 nm. The absorption maximum of tyrosine occurs at 274 nm.[3] Role in protein structure and functionAromatic amino acids stabilize folded structures of many proteins.[4][5] Aromatic residues are found predominantly sequestered within the cores of globular proteins, although often comprise key portions of protein-protein or protein-ligand interaction interfaces on the protein surface. Aromatic amino acids as precursorsAromatic amino acids often serve as the precursors to important biochemicals.
BiosynthesisShikimate pathwayIn plants, the shikimate pathway first leads to the formation of chorismate, which is the precursor of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. These aromatic amino acids are the precursors of many secondary metabolites, all essential to a plant's biological functions, such as the hormones salicylate and auxin. This pathway contains enzymes that can be regulated by inhibitors, which can cease the production of chorismate, and ultimately the organism's biological functions. Herbicides and antibiotics work by inhibiting these enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids, thereby rendering them toxic to plants.[7] Glyphosate, a type of herbicide, is used to control the accumulation of excess greens. In addition to destroying greens, Glyphosate can easily affect the maintenance of the gut microbiota in host organisms by specifically inhibiting the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase which prevents the biosynthesis of essential aromatic amino acids. Inhibition of this enzyme results in disorders such as gastrointestinal diseases and metabolic diseases.[8] 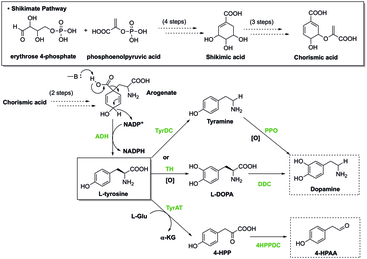 Nutritional requirementsAnimals obtain aromatic amino acids from their diet, but nearly[a] all plants and some micro-organisms must synthesize their aromatic amino acids through the metabolically costly shikimate pathway in order to make them. Histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, are essential amino acids for animals. Since they are not synthesized in the human body, they must be derived from the diet. Tyrosine is semi-essential; therefore, it can be synthesized by the animal, but only from phenylalanine. Phenylketonuria, a genetic disorder that occurs as a result of the inability to breakdown phenylalanine, is due to a lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. A dietary lack of tryptophan can cause stunted skeletal development.[9] Excessive intake of aromatic amino acids far beyond levels obtained through normal protein consumption might lead to hypertension,[10] something which could go un-noticed for a long time in healthy individuals. It could be caused by other factors as well such as the use of various herbs and foods like chocolate which inhibit monoamine oxidase enzymes to varying degrees, and also some medications. Aromatic trace amines like tyramine can displace norepinephrine from peripheral monoamine vesicles and in people taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) this occurs to the extent of being life threatening. Blue diaper syndrome is an autosomal recessive disease that is caused by poor tryptophan absorption in the body. See also
Notes
References
Further reading
External links
|