|
Arytenoid cartilage
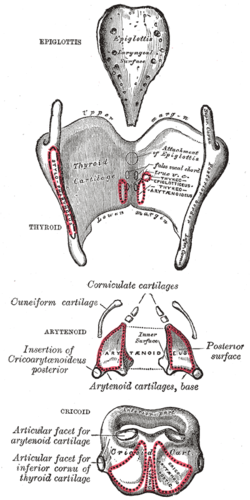
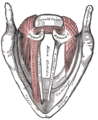
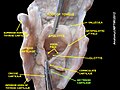
The arytenoid cartilages (/ærɪˈtiːnɔɪd/) are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoid cartilages allow for movement of the vocal cords by articulating with the cricoid cartilage. They may be affected by arthritis, dislocations, or sclerosis. StructureThe arytenoid cartilages are part of the posterior part of the larynx.[1] SurfacesThe posterior surface is triangular, smooth, concave, and gives attachment to the arytenoid muscle and transversus. The antero-lateral surface is somewhat convex and rough. On it, near the apex of the cartilage, is a rounded elevation (colliculus) from which a ridge (crista arcuata) curves at first backward and then downward and forward to the vocal process. The lower part of this crest intervenes between two depressions or foveæ, an upper, triangular, and a lower oblong in shape; the latter gives attachment to the thyroarytenoid muscle (vocal muscle). The medial surface is narrow, smooth, and flattened, covered by mucous membrane.[1] It forms the lateral boundary of the intercartilaginous part of the rima glottidis. Base and apexThe base of each cartilage is broad, and on it is a concave smooth surface, for articulation with the cricoid cartilage.
The apex of each cartilage is pointed, curved backward and medialward, and surmounted by a small conical, cartilaginous nodule, the corniculate cartilage. It articulates with the cricoid lamina with a ball-and-socket joint.[1] FunctionThe arytenoid cartilages allow the vocal folds to be tensed, relaxed, or approximated. They articulate with the supero-lateral parts of the cricoid cartilage lamina, forming the cricoarytenoid joints at which they can come together, move apart, tilt anteriorly or posteriorly, and rotate. Clinical significanceArthritisRheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis can affect the cricoarytenoid joint.[1] This can cause airway obstruction, which may be life-threatening.[1] DislocationRarely, the arytenoid cartilage may be dislocated.[2] This is most often caused by tracheal intubation,[2][3] major trauma to the larynx, [2] or more rarely a laryngeal mask airway.[4] This may cause symptoms with problems breathing, such as "breathiness" when breathing.[2] Electromyography and CT scans of the larynx may be used to assess a dislocation in detail.[2] Dislocations may be reduced using an endoscope.[2] Laryngeal cancerSome cases of laryngeal cancer cause the arytenoid cartilage to appear sclerotic.[5] This may be observed, and is highly predictive of laryngeal cancer.[5] HistoryEtymologyThe term "arytenoid" comes from Ancient Greek ἀρύταινα arytaina meaning "ladle" and εἶδος eidos, meaning "form".[6] They are also often described as "pyramid" shaped.[1] The word "arytenoid" is pronounced /ærɪˈtiːnɔɪd/.[7] Other animalsThe arytenoid cartilages are in the larynxes of many animals, including horses.[8] Additional images
References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||