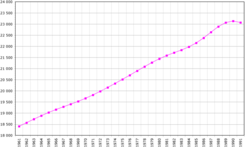
Demographics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia Yugoslavia demographics for 1945 to 1991
Yugoslavia population pyramid in 1991 Demographics of Yugoslavia (1961–1991), Data of FAO , year 2005 ; Number of inhabitants in thousands. Demographics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia , during its existence from 1945 until 1991, include population density , ethnicity , education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects. During its last census in 1991, Yugoslavia enumerated 23,528,230 people. Serbs had a plurality, followed by Croats , Bosniaks , Albanians , Slovenes and Macedonians .
Ethnic groups
Map of population density in Yugoslavia
Ethnic groups in Yugoslavia (1991)
Others combined (4.6%)
This is data from the last four Yugoslav censuses (1961, 1971, 1981, and 1991). Ethnic groups that were considered to be constitutive (explicitly mentioned in the constitution, and not considered minority or immigrant) appear in bold text.
Nationality
1961
%
1971
%
1981
%
1991
%
Serbs 7,806,152
42.1%
8,143,246
39.7%
8,140,507
36.3%
8,526,872
36.2%
Croats 4,293,809
23.2%
4,526,782
22.1%
4,428,043
19.7%
4,636,700
19.7%
Slav Muslims [ a] 972,960
5.3%
1,729,932
8.4%
1,999,890
8.9%
2,353,002
10.0%
Albanians
914,733
4.9%
1,309,523
6.4%
1,730,878
7.7%
2,178,393
9.3%
Slovenes 1,589,211
8.6%
1,678,032
8.2%
1,753,571
7.8%
1,760,460
7.5%
Macedonians 1,045,516
5.7%
1,194,784
5.8%
1,341,598
6.0%
1,372,272
5.8%
Yugoslavs 317,124
1.7%
273,077
1.3%
1,209,024
5.4%
710,394
3.0%
Montenegrins 513,832
2.8%
508,843
2.5%
579,043
2.6%
539,262
2.3%
Hungarians
504,369
2.7%
477,374
2.3%
426,867
1.9%
378,997
1.6%
Romani
78,485
0.4%
148,604
0.7%
n/a
n/a
Turks
127,920
0.6%
101,328
0.5%
n/a
n/a
Slovaks
83,656
0.4%
80,300
0.4%
n/a
n/a
Romanians
58,570
0.3%
54,721
0.2%
n/a
n/a
Bulgarians
58,627
0.3%
36,642
0.2%
n/a
n/a
Vlachs
21,990
0.1%
32,071
0.1%
n/a
n/a
Rusyns
24,640
0.1%
23,320
0.1%
n/a
n/a
Czechs
24,620
0.1%
19,609
0.1%
n/a
n/a
Italians
21,791
0.1%
15,116
0.1%
n/a
n/a
Ukrainians
13,972
0.1%
12,716
0.1%
n/a
n/a
Germans
12,875
0.1%
?
?
n/a
n/a
Russians
7,427
?
?
n/a
n/a
Jews
4,811
?
?
n/a
n/a
Poles
4,033
?
?
n/a
n/a
Greeks
1,564
?
?
n/a
n/a
other/not determined
591,585
3.2%
136,398
0.6%
302,254
1.5%
n/a
n/a
Total
18,549,291
100.00%
20,522,972
100.0%
22,438,331
100.00%
23,528,230
100.0%
Republics by population
Population of Yugoslavia by republics and provinces in 1991
Serbia
40.9%
Serbia proper
24.0%
Croatia
20.6%
Bosnia and Herzegovina
18.8%
Macedonia
8.8%
Vojvodina
8.6%
Kosovo
8.4%
Slovenia
8.2%
Montenegro
2.6%
The population data are from the 1991 census .
Rank
Republic/Province
Population 1991
%
1
Serbia 9,791,475
40.9%
---
Serbia proper 5,824,126
24.0%
2
Croatia 4,784,265
20.6%
3
Bosnia and Herzegovina 4,364,574
18.8%
4
Macedonia 2,033,964
8.8%
---
Vojvodina 2,012,605
8.6%
---
Kosovo 1,954,744
8.4%
5
Slovenia 1,962,606
8.2%
6
Montenegro 615,276
2.6%
Yugoslavia 23,528,230
100%
Republics by population density
Population density of Yugoslavia by republics and provinces in 1991
Kosovo
183.1
Serbia
114.0
Serbia proper
99.4
Slovenia
94.5
Vojvodina
92.8
Yugoslavia
92.6
Bosnia and Herzegovina
85.6
Croatia
84.6
Macedonia
79.1
Montenegro
44.5
Rank
Republic/Province
Population
Area (km2 )
Density
---
Kosovo 1,954,744
10,887
183.1
1
SR Serbia 9,791,475
88,361
114.0
---
Serbia proper 5,824,126
55,968
99.4
2
Slovenia 1,962,606
20,251
94.5
---
Vojvodina 2,012,605
21,506
92.8
3
Bosnia and Herzegovina 4,364,574
51,129
85.6
4
Croatia 4,784,265
56,538
84.6
5
Macedonia 2,033,964
25,713
79.1
6
Montenegro 615,276
13,810
44.5
Yugoslavia 23,528,230
255,804
92.6
Largest cities
According to the 1991 census, there were 19 cities in Yugoslavia with more than 100,000 inhabitants.
The population of these cities has developed as follows:
[ 5]
Population of the largest cities in Yugoslavia (in thousands)
City
1921
1953
1981
1991
Belgrad
111,7
470,2
1.145,0
1.168,0
Zagreb
108,3
350,8
768,7
933,9
Skopje
41,1
119,0
405,9
-
Sarajevo
60,1
111,7
-
415,6
Ljubljana
53,3
111,2
-
-
Split
25,0
61,2
169,3
189,4
Novi Sad
39,2
83,2
169,8
179,6
Niš
25,1
60,7
161,0
175,4
Rijeka
*
75,3
158,3
168,0
Kragujevac
15,7
40,6
87,0
147,3
Zenica
7,6
22,6
-
145,6
Banja Luka
18,0
30,4
123,8
142,6
Tuzla
14,2
25,0
65,0
131,9
Mostar
18,2
25,9
-
126,1
Titograd
8,7
13,6
95,8
117,8
Priština
14,3
24,1
69,5
108,1
Maribor
30,6
70,8
104,7
-
Osijek
34,4
57,4
104,2
104,8
Subotica
101,9
59,8
100,2
100,4
In addition to demographic changes, the incorporation of suburbs is also responsible for the changes in the number of inhabitants. Rijeka (Fiume) was still part of Italy in 1921.
Vital statistics
Vital statistics[ 6] [ 7]
Average population
Live births
Deaths
Natural change
Crude birth rate (per 1000)
Crude death rate (per 1000)
Natural change (per 1000)
Total fertility rate
Female fertile population (15–49 years)
1947
15,679,000
416,799
199,902
216,897
26.6
12.7
13.8
1948
15,901,032
446,634
214,015
232,619
28.1
13.5
14.6
1949
16,133,000
483,663
217,180
266,483
30.0
13.5
16.5
1950
16,339,860
492,993
212,165
280,828
30.2
13.0
17.2
3.77
4,411,195
1951
16,578,223
446,254
234,689
211,565
26.9
14.2
12.8
3.32
4,455,670
1952
16,793,498
498,172
197,520
300,652
29.7
11.8
17.9
3.65
4,500,131
1953
17,048,601
484,139
211,790
272,349
28.4
12.4
16.0
3.41
4,544,601
1954 [ 8] 17,284,632
493,567
187,521
306,046
28.6
10.8
17.7
3.40
4,600,326
1955 [ 9] 17,522,438
471,394
199,982
271,412
26.9
11.4
15.5
3.18
4,656,054
1956
17,690,580
460,235
198,497
261,738
26.0
11.2
14.8
3.04
4,711,776
1957
17,865,515
426,701
190,334
236,367
23.9
10.7
13.2
2.77
4,745,520
1958
18,034,999
432,399
166,801
265,598
24.0
9.2
14.7
2.79
4,749,438
1959
18,226,203
424,276
180,747
243,529
23.3
9.9
13.4
2.76
4,708,379
1960 [ 10] 18,402,257
432,595
182,693
249,902
23.5
9.9
13.6
2.83
4,689,628
1961
18,592,567
422,180
167,447
254,733
22.7
9.0
13.7
2.78
4,670,880
1962
18,815,935
413,093
186,843
226,250
22.0
9.9
12.0
2.68
4,766,916
1963
19,036,409
407,406
169,744
237,662
21.4
8.9
12.5
2.64
4,804,648
1964
19,260,364
401,104
181,255
219,849
20.8
9.4
11.4
2.62
4,861,010
1965 [ 11] 19,489,605
408,158
170,549
237,609
20.9
8.8
12.2
2.69
4,938,773
1966
19,739,122
399,802
159,570
240,232
20.3
8.1
12.2
2.64
5,043,670
1967
19,960,120
389,640
174,060
215,580
19.5
8.7
10.8
2.55
5,176,374
1968
20,121,246
382,543
174,800
207,743
19.0
8.7
10.3
2.47
5,291,934
1969
20,251,498
382,764
188,693
194,071
18.9
9.3
9.6
2.43
5,421,866
1970 [ 12] 20,386,272
363,278
181,843
181,435
17.8
8.9
8.9
2.27
5,492,906
1971
20,579,890
375,762
179,113
196,649
18.3
8.7
9.6
2.38
5,458,432
1972
20,797,221
380,743
190,578
190,165
18.3
9.2
9.1
2.36
5,518,843
1973
21,008,154
379,051
180,997
198,054
18.0
8.6
9.4
2.31
5,575,065
1974
21,223,359
382,947
177,691
205,256
18.0
8.4
9.7
2.29
5,596,395
1975 [ 13] 21,441,297
388,037
184,907
203,130
18.1
8.6
9.5
2.28
5,651,830
1976
21,674,043
392,364
182,965
209,399
18.1
8.4
9.7
2.26
5,684,130
1977
21,900,681
384,637
182,803
201,834
17.6
8.3
9.2
2.19
5,706,563
1978
22,121,687
381,387
191,087
190,300
17.2
8.6
8.6
2.16
5,720,058
1979
22,297,376
378,803
190,304
188,499
17.0
8.5
8.5
2.13
5,748,224
1980 [ 14] 22,359,500
382,120
197,369
184,751
17.1
8.8
8.3
2.14
5,776,387
1981
22,499,154
369,047
201,201
167,846
16.4
8.9
7.5
2.09
5,706,892
1982
22,646,153
378,814
203,272
175,542
16.7
9.0
7.8
2.14
5,686,451
1983
22,800,697
374,610
218,980
155,630
16.4
9.6
6.8
2.11
5,704,798
1984
22,954,868
377,362
214,725
162,637
16.4
9.4
7.1
2.11
5,729,944
1985 [ 15] 23,121,383
366,629
212,883
153,746
15.9
9.2
6.6
2.05
5,764,187
1986
23,259,342
359,626
213,149
146,477
15.5
9.2
6.3
2.00
5,830,545
1987
23,393,494
359,338
214,666
144,672
15.4
9.2
6.2
2.00
5,820,653
1988
23,526,195
356,268
213,466
142,802
15.1
9.1
6.1
1.98
5,838,991
1989
23,594,157
336,394
215,483
120,911
14.3
9.1
5.1
1.88
5,895,545
1990 [ 16] [ 17] 23,657,623
335,152
212,148
123,004
14.2
9.0
5.2
1.87
5,922,912
1991 [ 18] 23,532,279
325,922
221,929
103,993
13.8
9.4
4.4
1.94
5,669,046
Average population
Live births
Deaths
Natural change
Crude birth rate (per 1000)
Crude death rate (per 1000)
Natural change (per 1000)
Total fertility rate
Female fertile population (15–49 years)
Average population
Marriages
Divorces
Crude marriage rate (per 1000)
Crude divorce rate (per 1000)
Divorces per 1000 marriages
1947
15,679,000
205,835
20,915
13.1
1.3
101.6
1948
15,901,032
203,822
24,586
12.8
1.5
120.6
1949
16,133,000
184,078
16,985
11.4
1.1
92.3
1950
16,339,860
185,965
17,879
11.4
1.1
96.1
1951
16,578,223
170,133
15,538
10.3
0.9
91.3
1952
16,793,498
176,055
12,359
10.5
0.7
70.2
1953
17,048,601
167,940
16,020
9.9
0.9
95.4
1954
17,284,632
171,547
16,053
9.9
0.9
93.6
1955
17,522,438
162,711
19,389
9.3
1.1
119.2
1956
17,690,580
156,379
19,336
8.8
1.1
123.6
1957
17,865,515
154,970
20,421
8.7
1.1
131.8
1958
18,034,999
170,242
21,856
9.4
1.2
128.4
1959
18,226,203
163,572
21,483
9.0
1.2
131.3
1960
18,402,257
168,120
22,085
9.1
1.2
131.4
1961
18,592,567
168,510
21,532
9.1
1.2
127.8
1962
18,815,935
162,672
21,198
8.6
1.1
130.3
1963
19,036,409
157,909
21,328
8.3
1.1
135.1
1964
19,260,364
166,998
21,405
8.7
1.1
128.2
1965
19,489,605
174,301
21,649
8.9
1.1
124.2
1966
19,739,122
168,789
23,042
8.6
1.2
136.5
1967
19,960,120
169,282
20,840
8.5
1.0
123.1
1968
20,121,246
170,470
20,984
8.5
1.0
123.1
1969
20,251,498
174,507
20,178
8.6
1.0
115.6
1970
20,386,272
182,704
20,473
9.0
1.0
112.1
1971
20,579,890
183,916
21,347
8.9
1.0
116.1
1972
20,797,221
186,156
22,040
9.0
1.1
118.4
1973
21,008,154
183,665
23,221
8.7
1.1
126.4
1974
21,223,359
181,192
24,802
8.5
1.2
136.9
1975
21,441,297
180,046
25,137
8.4
1.2
139.6
1976
21,674,043
174,918
24,431
8.1
1.1
139.7
1977
21,900,681
178,783
22,990
8.2
1.0
128.6
1978
22,121,687
178,819
24,180
8.1
1.1
135.2
1979
22,297,376
176,310
21,952
7.9
1.0
124.5
1980
22,359,500
171,439
22,583
7.7
1.0
131.7
1981
22,499,154
173,036
22,557
7.7
1.0
130.4
1982
22,646,153
172,359
22,715
7.6
1.0
131.8
1983
22,800,697
171,906
22,127
7.5
1.0
128.7
1984
22,954,868
167,789
22,260
7.3
1.0
132.7
1985
23,121,383
163,022
23,952
7.1
1.0
146.9
1986
23,259,342
160,277
22,557
6.9
1.0
140.7
1987
23,393,494
163,469
22,907
7.0
1.0
140.1
1988
23,526,195
160,419
23,127
6.8
1.0
144.2
1989
23,594,157
158,544
22,761
6.7
1.0
143.6
1990
23,657,623
146,975
20,551
6.2
0.9
139.8
1991
23,532,279
134,826
17,551
5.7
0.7
130.2
Average population
Marriages
Divorces
Crude marriage rate (per 1000)
Crude divorce rate (per 1000)
Divorces per 1000 marriages
History of national minorities in SFR Yugoslavia
1940s and 1950s
The SFRY recognised "nations" (narodi) and "nationalities" (narodnosti) separately; the former included the constituent Slavic peoples, while the latter included other Slavic and non-Slavic ethnic groups such as Bulgarians and Slovaks (Slavic); and Hungarians and Albanians (non-Slavic). About a total of 26 known ethnic groups were known to live in Yugoslavia, including non-European originated Romani people .
Some of the largest non-Slavic ethnic minorities – Hungarians of Serbia , Germans (predominantly Danube Swabians ), Kosovar Albanians and Istrian Italians – had been considered "troublesome" by Yugoslav authorities already in the first, interwar Yugoslavia, in part for supporting their ethnic interests and nation states as opposed to pan-Slavic ambitions during World War I .
[ 20] Minority rights of non-Slavs were neither guaranteed nor upheld, but rather stifled if they had proved "anti-Yugoslavian". Education in Hungarian and German was limited, a number of Hungarian and German cultural societies had been banned in the Kingdom until the late 1930s, when the country drifted towards pro-axis positions. Nonetheless, local Germans collaborated with the Nazi occupation forces during World War II, and ethnic Hungarians generally welcomed the return of Bačka region to Hungary. The Yugoslav communist partisan movement was unpopular among those minorities, with the German Ernst Thälmann unit existing merely on paper and the Hungarian Petőfi unit numbering mere hundred men. After the occupation forces were pushed out of Yugoslavia, tens of thousands of Germans, Hungarians and Italians were either imprisoned in labor camps (such as Goli Otok prison ) or executed in summary executions .
After World War II, around 250,000 Germans and Italians were expelled or fled from the country, fearing reprisals, their property confiscated, in the events known as the expulsion of Germans after World War II and Istrian–Dalmatian exodus , the latter in the newly annexed areas in Istria and Rijeka , as well as from Dalmatia . Hundreds (several thousands, according to some estimates) were summarily killed in the process. The same befell Hungarians, who faced mass murders in Vojvodina . Modern estimates vary about 35 000 - 40 000 Hungarians killed. After the war, however, free education in the native languages of the minorities were guaranteed by the Communist constitution.
During the era of Tito–Stalin split , many Hungarians (who in 1953 made up around 25% of the population in Vojvodina) were sympathetic towards the Hungarian People's Republic , and the words of Radio Budapest spread among the villagers.
In 1950s, various ethnic stereotypes about specific nations in the country were commonly recounted and circulated in the media. Bulgarians were reported to be a "poor and backward minority", while in contrast, Czechs and Slovaks were "industrious and valuable minorities" for Yugoslavia. Some Czechs and Slovaks also emigrated after the war, but a "large number" of them returned after communists seized power in Czechoslovakia in 1948.
See also
References
^ For 1921: Brockhaus 15th edition; For 1953: Enciklopedija Jugoslavije 1st edition, volume 4, p. 599; For 1981: Brockhaus 19th edition (in the table in the article "Yugoslavia" there are incorrect details for Belgrade, Zagreb, Sarajevo and Ljubljana due to the inclusion of the agglomerations); For 1991: Brockhaus 20th edition
^ "Eurostat/Database/Population and social conditions/Demography and migration(demo)" .^ "Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia" .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1954" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1955" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1960" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1965" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1970" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1975" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1980" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1985" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1990" (PDF) .^ "Demography statistics 1990,Yugoslavia" (PDF) .^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia,1991" (PDF) .^ Yugoslavia's National Minorities under Communism by Paul Shoup In: Slavic Review, Vol. 22, No. 1 (Mar., 1963), pp. 64-81
Books
Journals