Counties of Ohio There are 88 counties in the U.S. state of Ohio . Nine of them existed at the time of the Ohio Constitutional Convention in 1802.[ 1] Wayne , was established on August 15, 1796, and encompassed roughly the present state of Michigan .[ 2] Wayne County is in northeastern Ohio, considerably distant from the area that was the original Wayne County.[ 1]
The Ohio Constitution allows counties to set up a charter government as many cities and villages do,[ 3] Summit and Cuyahoga counties have done so,[ 4] [ 5] home rule powers and can do only what has been expressly authorized by the Ohio General Assembly . The elected county officials in Ohio county governments include three commissioners , a sheriff (the highest law enforcement officer in the county); prosecutor (equivalent of a district attorney in other states); coroner , engineer, Recorder, auditor , treasurer , and clerk of courts .[ 6] [ 7]
Population figures are based on the 2023 vintage Census population estimates. The population of Ohio was 11,785,935 at that time, a decrease of 0.1% from 2020. The average population of Ohio's counties was 133,931; Franklin County was the most populous (1,326,063) and Vinton County was the least (12,474). The average land area is 464 sq mi (1,200 km2 ). The largest county by area is Ashtabula County at 702.44 sq mi (1,819.3 km2 ), and its neighbor, Lake County , is the smallest at 228.21 sq mi (591.1 km2 ). The total area of the state is 40,860.69 sq mi (105,828.7 km2 ).[ 8] [ 9]
List of counties
County
FIPS code[ 10] County Seat[ 11]
Est. [ 12] Origin[ 13]
Etymology[ 12] [ 13]
Population[ 10] [ 11] [ 14]
Area[ 11]
Map
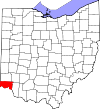
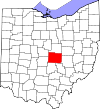
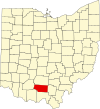
Adams County
001
West Union Jul 10, 1797 Hamilton County
John Adams (1735–1826), President of the United States when the county was organized
27,521
583.91 sq mi1,512 km2 )
Allen County
003
Lima Mar 1, 1820 Shelby County
John Allen (1771/2-1813), a War of 1812 colonel[ 15] 100,838
404.43 sq mi1,047 km2 )
Ashland County
005
Ashland Feb 24, 1846 Wayne, Richland, Huron, and Lorain Counties
Ashland , home of U.S. Senator from Kentucky Henry Clay
52,190
424.37 sq mi1,099 km2 )
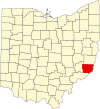
Ashtabula County
007
Jefferson Jun 7, 1807 Trumbull and Geauga Counties
Ashtabula River , which means "fish river" in an Algonquian language [ 16] 96,845
702.44 sq mi1,819 km2 )
Athens County
009
Athens Mar 1, 1805 Washington County
Athens in Greece
62,706
506.76 sq mi1,313 km2 )
Auglaize County
011
Wapakoneta Feb 14, 1848 Allen, Mercer, Darke, Hardin, Logan, Shelby, and Van Wert Counties
Auglaize River , which means "fallen timbers river" in the Shawnee Indian language
46,050
401.25 sq mi1,039 km2 )
Belmont County
013
St. Clairsville Sep 7, 1801 Jefferson and Washington Counties
French for "beautiful mountain"
64,918
537.35 sq mi1,392 km2 )
Brown County
015
Georgetown Mar 1, 1818 Adams and Clermont Counties
General Jacob Brown (1775–1828), an officer of the War of 1812
43,777
491.76 sq mi1,274 km2 )
Butler County
017
Hamilton May 1, 1803 Hamilton County
General Richard Butler (1743–1791), killed at the Battle of the Wabash
393,043
467.27 sq mi1,210 km2 )
Carroll County
019
Carrollton Jan 1, 1833 Columbiana, Stark, Harrison, Jefferson, and Tuscarawas Counties
Charles Carroll (1737–1832), last surviving signer of the United States Declaration of Independence
26,758
394.67 sq mi1,022 km2 )
Champaign County
021
Urbana Mar 1, 1805 Greene and Franklin Counties
French for "a plain", describing the land in the area
38,845
428.56 sq mi1,110 km2 )
Clark County
023
Springfield Mar 1, 1818 Champaign, Madison, and Greene Counties
General George Rogers Clark (1752–1818), defeated the Shawnee Indians in a battle near the Springfield area
134,610
399.86 sq mi1,036 km2 )
Clermont County
025
Batavia Dec 6, 1800 Hamilton County
French for "clear mountain"
211,972
451.99 sq mi1,171 km2 )
Clinton County
027
Wilmington Mar 1, 1810 Highland and Warren Counties
George Clinton (1739–1812), vice-president when the county was organized
41,938
410.88 sq mi1,064 km2 )
Columbiana County
029
Lisbon May 1, 1803 Jefferson and Washington Counties
Christopher Columbus , European explorer of the Americas
100,182
532.46 sq mi1,379 km2 )
Coshocton County
031
Coshocton Jan 31, 1810 Muskingum and Tuscarawas Counties
Delaware Indian word meaning "union of waters"
36,869
564.07 sq mi1,461 km2 )
Crawford County
033
Bucyrus Apr 1, 1820 Delaware County
Colonel William Crawford (1732–1782), Revolutionary War officer
41,529
402.11 sq mi1,041 km2 )
Cuyahoga County
035
Cleveland Jun 7, 1807 Geauga County
Cuyahoga River , which means "crooked river" in an Iroquoian language [ 17] 1,233,088
458.49 sq mi1,187 km2 )
Darke County
037
Greenville Jan 3, 1809 Miami County
General William Darke (1736–1801), Revolutionary War officer
51,415
599.80 sq mi1,553 km2 )
Defiance County
039
Defiance Apr 7, 1845 Williams, Henry, and Paulding Counties
Fort Defiance , built in 1794 by General Anthony Wayne
38,315
411.16 sq mi1,065 km2 )
Delaware County
041
Delaware Apr 1, 1808 Franklin County
Delaware Indians
231,636
442.41 sq mi1,146 km2 )
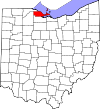
Erie County
043
Sandusky Mar 15, 1838 Huron and Sandusky Counties
Erie Indians
74,035
254.88 sq mi660 km2 )
Fairfield County
045
Lancaster Dec 9, 1800 Ross and Washington Counties
Named for the beauty of its "fair fields"
165,360
505.11 sq mi1,308 km2 )
Fayette County
047
Washington Court House Mar 1, 1810 Ross and Highland Counties
Gilbert du Motier, marquis de La Fayette , French military officer and aristocrat who participated in both the American and French revolutions
28,817
406.58 sq mi1,053 km2 )
Franklin County
049
Columbus Apr 30, 1803 Ross and Wayne Counties
Benjamin Franklin (1706–1791), Founding Father , author, printer, political theorist, scientist, inventor, and statesman
1,326,063
539.87 sq mi1,398 km2 )
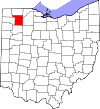
Fulton County
051
Wauseon Apr 1, 1850 Lucas, Henry, and Williams Counties
Robert Fulton (1765–1815), inventor of the steamboat [ 18] 42,007
406.78 sq mi1,054 km2 )
Gallia County
053
Gallipolis Apr 30, 1803 Washington and Adams Counties
Gaul , the ancient name of France
28,986
468.78 sq mi1,214 km2 )
Geauga County
055
Chardon Mar 1, 1806 Trumbull County
A native american word meaning "raccoon"
95,407
403.66 sq mi1,045 km2 )
Greene County
057
Xenia May 1, 1803 Hamilton and Ross Counties
General Nathanael Greene (1742–1786), Revolutionary War officer
169,691
414.88 sq mi1,075 km2 )
Guernsey County
059
Cambridge Mar 1, 1810 Belmont and Muskingum Counties
Island of Guernsey , from where most of the settlers originated
38,089
521.90 sq mi1,352 km2 )
Hamilton County
061
Cincinnati Jan 2, 1790 One of the original counties
Alexander Hamilton (1755/7-1804), Secretary of the Treasury when the county was organized
827,058
407.36 sq mi1,055 km2 )
Hancock County
063
Findlay Apr 1, 1820 Logan County
John Hancock (1737–1793), president of the Continental Congress
74,704
531.35 sq mi1,376 km2 )
Hardin County
065
Kenton Apr 1, 1820 Logan County
General John Hardin (1753–1792), Revolutionary War officer
30,368
470.29 sq mi1,218 km2 )
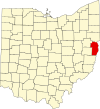
Harrison County
067
Cadiz Feb 1, 1813 Jefferson and Tuscarawas Counties
General William Henry Harrison (1773–1841), an officer of the War of 1812 and future President of the United States
14,159
403.53 sq mi1,045 km2 )
Henry County
069
Napoleon Apr 1, 1820 Shelby County
Patrick Henry (1736–1799), Revolutionary War -era legislator, orator, and scholar
27,520
416.50 sq mi1,079 km2 )
Highland County
071
Hillsboro May 1, 1805 Ross, Adams, and Clermont Counties
Descriptive of the county's terrain
43,614
553.28 sq mi1,433 km2 )
Hocking County
073
Logan Mar 1, 1818 Athens, Ross, and Fairfield Counties
Possibly derived from the Delaware Indian word "Hoch-Hoch-ing", meaning "bottle"
27,540
422.75 sq mi1,095 km2 )
Holmes County
075
Millersburg Jan 20, 1824 Coshocton, Wayne, and Tuscarawas Counties
Major Andrew Holmes (died 1814), a War of 1812 officer
44,386
422.99 sq mi1,096 km2 )
Huron County
077
Norwalk Mar 7, 1809 Portage and Cuyahoga Counties
Huron Indians
58,199
492.69 sq mi1,276 km2 )
Jackson County
079
Jackson Mar 1, 1816 Scioto, Gallia, Athens, and Ross Counties
General Andrew Jackson (1767–1845), future President of the United States
32,606
420.28 sq mi1,089 km2 )
Jefferson County
081
Steubenville Jul 29, 1797 Washington County
Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), Vice President when the county was organized, future President of the United States , and principal author of the Declaration of Independence
64,026
409.61 sq mi1,061 km2 )
Knox County
083
Mount Vernon Mar 1, 1808 Fairfield County
General Henry Knox , the first Secretary of War
63,320
527.12 sq mi1,365 km2 )
Lake County
085
Painesville Mar 6, 1840 Geauga and Cuyahoga Counties
Its location on Lake Erie
231,640
228.21 sq mi591 km2 )
Lawrence County
087
Ironton Dec 21, 1815 Gallia and Scioto Counties
Captain James Lawrence (1781–1813), naval hero in the War of 1812
56,118
454.96 sq mi1,178 km2 )
Licking County
089
Newark Mar 1, 1808 Fairfield County
Licking River , named for the salt licks in the area, or an English pronunciation of the Lenape word W'li/'ik'/nk meaning "where the flood waters recede"[ 19] 183,201
686.50 sq mi1,778 km2 )
Logan County
091
Bellefontaine Mar 1, 1818 Champaign County
General Benjamin Logan (c. 1742 – 1802), who destroyed Shawnee Indian towns in the county
46,057
458.44 sq mi1,187 km2 )
Lorain County
093
Elyria Dec 26, 1822 Huron, Cuyahoga, and Medina Counties
Province of Lorraine , France
317,910
492.50 sq mi1,276 km2 )
Lucas County
095
Toledo Jun 20, 1835 Wood, Sandusky, and Huron Counties
Robert Lucas (1781–1853), Governor of Ohio when the county was created
425,484
340.46 sq mi882 km2 )
Madison County
097
London Mar 1, 1810 Franklin County
James Madison (1751–1836), fourth President of the United States
44,602
465.44 sq mi1,205 km2 )
Mahoning County
099
Youngstown Mar 1, 1846 Columbiana and Trumbull Counties
Mahoning River , from a Lenape word meaning "at the licks"
225,596
415.25 sq mi1,075 km2 )
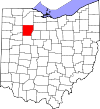
Marion County
101
Marion Apr 1, 1820 Delaware County
General Francis Marion (1732–1795), lieutenant colonel in the Continental Army and later brigadier general in the American Revolutionary War
64,851
403.84 sq mi1,046 km2 )
Medina County
103
Medina Feb 18, 1812 Portage County
Medina , world-renowned religious site in western Saudi Arabia
184,042
423 sq mi1,096 km2 )
Meigs County
105
Pomeroy Apr 1, 1819 Gallia and Athens Counties
Return Jonathan Meigs Jr. (1764–1825), Governor of Ohio and Postmaster General at the time the county was organized
21,767
429.42 sq mi1,112 km2 )
Mercer County
107
Celina Apr 1, 1820 Darke County
General Hugh Mercer (1726–1777), a Revolutionary War officer
42,439
463.27 sq mi1,200 km2 )
Miami County
109
Troy Mar 1, 1807 Montgomery County
Miami Indians
110,876
407.04 sq mi1,054 km2 )
Monroe County
111
Woodsfield Jan 29, 1813 Belmont, Washington, and Guernsey Counties
James Monroe (1758–1831), Secretary of State when the county was organized and future President of the United States
13,153
455.54 sq mi1,180 km2 )
Montgomery County
113
Dayton May 1, 1803 Hamilton and Wayne Counties
General Richard Montgomery (1738–1775), a Revolutionary War officer
533,796
461.68 sq mi1,196 km2 )
Morgan County
115
McConnelsville Dec 29, 1817 Washington, Guernsey, and Muskingum Counties
General Daniel Morgan (c. 1735 – 1802), a Revolutionary War officer
13,646
417.66 sq mi1,082 km2 )
Morrow County
117
Mount Gilead Mar 1, 1848 Knox, Marion, Delaware, and Richland Counties
Jeremiah Morrow (1771–1852), Governor of Ohio
35,595
406.22 sq mi1,052 km2 )
Muskingum County
119
Zanesville March 1, 1804
Washington and Fairfield Counties
An Indian word meaning "A town by the river" or "by the river side"
86,305
664.63 sq mi1,721 km2 )
Noble County
121
Caldwell Apr 1, 1851 Monroe, Washington, Morgan, and Guernsey Counties
James Noble, an early settler in the area
14,311
399.00 sq mi1,033 km2 )
Ottawa County
123
Port Clinton Mar 6, 1840 Erie, Sandusky, and Lucas Counties
Named for the Ottawa Indians ; Ottawa means "trader" in their language
39,803
254.95 sq mi660 km2 )
Paulding County
125
Paulding Apr 1, 1820 Darke County
John Paulding (1758–1818), captor of spy John André during the Revolutionary War
18,706
416.26 sq mi1,078 km2 )
Perry County
127
New Lexington Mar 1, 1818 Washington, Fairfield, and Muskingum Counties
Commodore Oliver Hazard Perry (1785–1819), a naval officer of the War of 1812
35,551
409.78 sq mi1,061 km2 )
Pickaway County
129
Circleville Mar 1, 1810 Ross, Fairfield, and Franklin Counties
A misspelling of the Piqua tribe, a branch of the Shawnee
61,086
501.91 sq mi1,300 km2 )
Pike County
131
Waverly Feb 1, 1815 Ross, Scioto, and Adams Counties
General Zebulon M. Pike (1779–1813), a War of 1812 officer and discoverer of Pikes Peak in Colorado in 1806
27,001
441.49 sq mi1,143 km2 )
Portage County
133
Ravenna Jun 7, 1807 Trumbull County
Derived from an Indian portage
162,665
492.39 sq mi1,275 km2 )
Preble County
135
Eaton Mar 1, 1808 Montgomery and Butler Counties
Captain Edward Preble (1761–1807), a Naval commander in the Revolutionary War
40,556
424.80 sq mi1,100 km2 )
Putnam County
137
Ottawa Apr 1, 1820 Shelby County
General Israel Putnam (1718–1790), a Revolutionary War officer
34,199
483.87 sq mi1,253 km2 )
Richland County
139
Mansfield Mar 1, 1808 Fairfield County
Descriptive of the soil in the area
125,064
496.88 sq mi1,287 km2 )
Ross County
141
Chillicothe Aug 20, 1798 Adams and Washington Counties
Named for U.S. Senator from Pennsylvania James Ross by territorial governor Arthur St. Clair
76,501
688.41 sq mi1,783 km2 )
Sandusky County
143
Fremont Apr 1, 1820 Huron County
An Iroquois word meaning "cold water"
58,709
409.18 sq mi1,060 km2 )
Scioto County
145
Portsmouth May 1, 1803 Adams County
Scioto River ; Scioto is a Wyandot Indian word meaning "deer"
71,969
612.27 sq mi1,586 km2 )
Seneca County
147
Tiffin Apr 1, 1820 Huron County
Seneca Indians, who had a reservation in the county area at the time
54,527
550.59 sq mi1,426 km2 )
Shelby County
149
Sidney Apr 1, 1819 Miami County
General Isaac Shelby (1750–1826), a Revolutionary War officer and Governor of Kentucky
47,765
409.27 sq mi1,060 km2 )
Stark County
151
Canton Feb 13, 1808 Columbiana County
General John Stark (1728–1822), a Revolutionary War officer; known as the "Hero of Bennington" for his exemplary service at the Battle of Bennington in 1777
372,716
576.14 sq mi1,492 km2 )
Summit County
153
Akron Mar 3, 1840 Medina, Portage, and Stark Counties
Its location at the highest elevation along the Ohio and Erie Canal
535,733
419.38 sq mi1,086 km2 )
Trumbull County
155
Warren Jul 10, 1800 Jefferson and Wayne Counties
Jonathan Trumbull (1710–1785), Governor of Connecticut when the county was organized
200,373
616.48 sq mi1,597 km2 )
Tuscarawas County
157
New Philadelphia Mar 15, 1808 Muskingum County
Tuscarawas River , meaning "open mouth river"or 91,874
567.58 sq mi1,470 km2 )
Union County
159
Marysville Apr 1, 1820 Delaware, Franklin, Logan, and Madison Counties
Its formation by a union of four counties
69,637
436.65 sq mi1,131 km2 )
Van Wert County
161
Van Wert Apr 1, 1820 Darke County
Isaac Van Wart (1760–1828), captor of spy John André during the Revolutionary War
28,704
410.09 sq mi1,062 km2 )
Vinton County
163
McArthur Mar 23, 1850 Athens, Gallia, Hocking, Jackson, and Ross Counties
Samuel Finley Vinton (1792–1862), Ohio Statesman and U.S. Congressman
12,474
414.08 sq mi1,072 km2 )
Warren County
165
Lebanon May 1, 1803 Hamilton County
General Joseph Warren (1741–1775), a Revolutionary War officer
252,148
399.63 sq mi1,035 km2 )
Washington County
167
Marietta Jul 27, 1788 One of the original counties
George Washington (1732–1799), commander of the Continental Army , president of the Constitutional Convention , and future President of the United States
58,577
635.15 sq mi1,645 km2 )
Wayne County
169
Wooster Mar 1, 1812 Stark County
General Anthony Wayne (1745–1796), a Revolutionary War officer
116,510
555.36 sq mi1,438 km2 )
Williams County
171
Bryan Apr 1, 1820 Darke County
David Williams (1754–1831), captor of spy John André during the Revolutionary War
36,591
421.74 sq mi1,092 km2 )
Wood County
173
Bowling Green Apr 1, 1820 Refactored from non-county territory
Eleazer D. Wood (1783–1814), founder of Fort Meigs
132,650
617.32 sq mi1,599 km2 )
Wyandot County
175
Upper Sandusky Feb 3, 1845 Marion, Crawford, and Hardin Counties
Wyandot Indians
21,457
405.61 sq mi1,051 km2 )
List of county codes
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) is used by the U.S. government to uniquely identify counties. In the following table, these codes link to the United States Census Bureau's "quick facts" for each county. Ohio's FIPS code of 39 is used to distinguish from counties in other states. For example, Adams County's unique nationwide identifier is 39001.[ 10]
Various state agencies identify counties by different coding schemes. The Ohio Department of Taxation assigns consecutive numbers for the purpose of enumerating taxing districts.[ 22] Ohio Department of Public Safety , including the Ohio Bureau of Motor Vehicles , associates these county numbers with vehicle registrations.[ 23] Department of Transportation uses three-letter abbreviations in road inventory and traffic management applications.[ 24] Ohio History Connection refers to counties by two- and three-letter abbreviations in the Ohio Archaeological Inventory and Ohio Historic Inventory, respectively.[ 25]
See also
References
^ a b Laning, J.F. (1896). "The Evolution of Ohio Counties" . Ohio Archaeological and Historical Publications V : 326–350. Archived from the original on November 21, 2015.ISBN 1249686741 and Google Books ^ Lawyer, James Patterson (1905). History of Ohio: From the Glacial Period to the Present Time . Retrieved August 18, 2007 . ISBN 9781279183281 ^ Steinglass, Steven; Scarselli, Gino (2004). The Ohio State Constitution A Reference Guide . Westport, CT: Praeger Publishers. pp. 272–273. ISBN 0313267650 and Google Books ^ "Ohio Counties" . County of Summit. November 15, 2011. Archived from the original on January 27, 2020. Retrieved February 28, 2013 .{{cite web }}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link )^ "Issue 6 reform wins big and sets in motion even bigger changes for Cuyahoga County" . cleveland.com. November 4, 2009. Retrieved January 28, 2010 .^ "OSBA - OSBA Staff Directory" . www.ohiobar.org .^ "Title 3 - Ohio Revised Code | Ohio Laws" .^ "Ohio QuickFacts" . U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on March 3, 2013. Retrieved February 27, 2013 .^ "Population Estimates" . U.S. Census Bureau. December 2009. Archived from the original on March 22, 2009. Retrieved February 27, 2013 .^ a b c "County FIPS Code Listing for the State of OHIO" . United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved July 9, 2016 .^ a b c "NACo - Find a County" . Archived from the original on April 13, 2007. Retrieved July 22, 2007 .^ a b "Federal Roster: Counties of Ohio, Derivation of Name and Date of Erection" (PDF) . Archived from the original on July 12, 2013. Retrieved July 21, 2013 .{{cite web }}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link )^ a b Howe, Henry (1891). Historical Collections of Ohio . Vol. 2. Columbus, OH: Henry Howe and Son. ISBN 1425565735 and Google Books ^ https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/OH/PST045223 [bare URL ^ Resolution of 111th Ohio General Assembly designating John Allen as the person for which Allen County was named .^ Ashtabula , Encyclopædia Britannica , 2007. Accessed November 19, 2007.^ Cuyahoga River , Encyclopædia Britannica , 2007. Accessed November 19, 2007.^ About Fulton County ^ Mahr, August C. (April 1957). "Indian River and Place Names in Ohio" . Ohio Archaeological and Historical Quarterly . 66 (2): 146–148. ^ a b "Ohio Counties with County Number" (PDF) . Columbus, Ohio: Ohio Department of Taxation. June 25, 2020. Retrieved September 11, 2023 .^ a b Taxing District Code Book 2023 (PDF) . Ohio Bureau of Motor Vehicles, Tax Distribution Section. January 3, 2023. Retrieved September 12, 2023 .^ a b "ODOT County Abbreviation Table" (PDF) . Ohio Department of Transportation. May 1, 2013. Retrieved December 21, 2014 .^ a b c "Ohio Archaeological Inventory Form Instruction Manual" (PDF) . Ohio Historic Preservation Office . June 2003. p. 61. Retrieved September 12, 2023 .
Further reading