|
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian (endonym: lietuvių kalba, pronounced [lʲiəˈtʊvʲuː kɐɫˈbɐ]) is an East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million[2] native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 1 million speakers elsewhere. Around half a million inhabitants of Lithuania of non-Lithuanian background speak Lithuanian daily as a second language. Lithuanian is closely related to neighbouring Latvian, though the two languages are not mutually intelligible. It is written in a Latin script. In some respects, some linguists consider it to be the most conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages.[3][4][5] History
Among Indo-European languages, Lithuanian is conservative in its grammar and phonology, retaining archaic features otherwise found only in ancient languages such as Sanskrit[7] (particularly its early form, Vedic Sanskrit) or Ancient Greek. Thus, it is an important source for the reconstruction of the Proto-Indo-European language despite its late attestation (with the earliest texts dating only to c. 1500 AD, whereas Ancient Greek was first written down about three thousand years earlier in c. 1450 BC).[8]  According to hydronyms of Baltic origin, the Baltic languages were spoken in a large area east of the Baltic Sea, and in c. 1000 BC it had two linguistic units: western and eastern.[9] According to glottochronological research, the Eastern Baltic languages split from the Western Baltic ones between c. 400 BC and c. 600 BC.[10][11] The Greek geographer Ptolemy had already written of two Baltic tribe/nations by name, the Galindai (Γαλίνδαι) and Sudinoi (Σουδινοί), in the 2nd century AD.[12][13] Lithuanian originated from the Eastern Baltic subgroup and remained nearly unchanged until c. 1 AD, however in c. 500 AD the language of the northern part of Eastern Balts was influenced by the Finnic languages, which fueled the development of changes from the language of the Southern Balts (see: Latgalian, which developed into Latvian, and extinct Curonian, Semigallian, and Selonian).[9] The language of Southern Balts was less influenced by this process and retained many of its older features, which form Lithuanian.[9]  The differentiation between Lithuanian and Latvian started after c. 800 AD; for a long period, they could be considered dialects of a single language.[14] At a minimum, transitional dialects existed until the 14th or 15th century and perhaps as late as the 17th century.[14][15] The German Livonian Brothers of the Sword occupied the western part of the Daugava basin, which resulted in colonization of the territory of modern Latvia (at the time it was called Terra Mariana) by Germans and had a significant influence on the language's independent development due to Germanisation (see also: Baltic Germans and Baltic German nobility).[14][16] There was fascination with the Lithuanian people and their language among the late 19th-century researchers, and the philologist Isaac Taylor wrote the following in his The Origin of the Aryans (1892):
Lithuanian was studied by several linguists such as Franz Bopp, August Schleicher, Adalbert Bezzenberger, Louis Hjelmslev,[18] Ferdinand de Saussure,[19] Winfred P. Lehmann and Vladimir Toporov,[20] Jan Safarewicz,[21] and others. By studying place names of Lithuanian origin, linguist Jan Safarewicz concluded that the eastern boundaries of Lithuanian used to be in the shape of zigzags through Grodno, Shchuchyn, Lida, Valozhyn, Svir, and Braslaw.[9] Such eastern boundaries partly coincide with the spread of Catholic and Orthodox faith, and should have existed at the time of the Christianization of Lithuania in 1387 and later.[9] Safarewicz's eastern boundaries were moved even further to the south and east by other scholars (e.g. Mikalay Biryla, Petras Gaučas, Jerzy Ochmański, Aleksandras Vanagas, Zigmas Zinkevičius, and others).[9] Proto-Balto-Slavic branched off directly from Proto-Indo-European, then sub-branched into Proto-Baltic and Proto-Slavic. Proto-Baltic branched off into Proto-West Baltic and Proto-East Baltic.[22] The Baltic languages passed through a Proto-Balto-Slavic stage, from which the Baltic languages retain exclusive and non-exclusive lexical, morphological, phonological and accentual isoglosses in common with the Slavic languages, which represent their closest living Indo-European relatives. Moreover, with Lithuanian being so archaic in phonology, Slavic words can often be deduced from Lithuanian by regular sound laws; for example, Lith. vilkas and Polish wilk ← PBSl. *wilkás (cf. PSl. *vьlkъ) ← PIE *wĺ̥kʷos, all meaning "wolf". Initially, Lithuanian was a spoken language in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Duchy of Prussia, while the beginning of Lithuanian writing is possibly associated with the introduction of Christianity in Lithuania when Mindaugas was baptized and crowned King of Lithuania in 1250–1251.[23][9] It is believed that prayers were translated into the local dialect of Lithuanian by Franciscan monks during the baptism of Mindaugas, however none of the writings has survived.[23] The first recorded Lithuanian word, reported to have been said on 24 December 1207 from the chronicle of Henry of Latvia, was Ba, an interjection of a Lithuanian raider after he found no loot to pillage in a Livonian church.[24] Lithuanian was mentioned as one of the languages of the participants of the Council of Constance in 1414–1418: see Lingwa Lietowia (left) and Littowelch (right) in a 15th century Chronik des Konstanzer Konzils compiled by Ulrich of Richenthal. Although no writings in Lithuanian have survived from the 15th century or earlier,[23] Lithuanian (Latin: Lingwa Lietowia) was mentioned as one of the European languages of the participants in the Council of Constance in 1414–1418.[25][26][27] From the middle of the 15th century, the legend spread about the Roman origin of the Lithuanian nobility (from the Palemon lineage), and the closeness of the Lithuanian language and Latin, thus this let some intellectuals in the mid-16th century to advocate for replacement of Ruthenian with Latin, as they considered Latin as the native language of Lithuanians.[28][29] Initially, Latin and Church Slavonic were the main written (chancellery) languages of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, but in the late 17th century – 18th century Church Slavonic was replaced with Polish.[23][30] Nevertheless, Lithuanian was a spoken language of the medieval Lithuanian rulers from the Gediminids dynasty and its cadet branches: Kęstutaičiai and Jagiellonian dynasties.[31][32][33][34] It is known that Jogaila, being ethnic Lithuanian by the male-line, himself knew and spoke Lithuanian with Vytautas the Great, his cousin from the Gediminids dynasty.[32][33][35] During the Christianization of Samogitia none of the clergy, who arrived to Samogitia with Jogaila, were able to communicate with the natives, therefore Jogaila himself taught the Samogitians about Catholicism; thus he was able to communicate in the Samogitian dialect of Lithuanian.[36] Soon afterwards Vytautas the Great wrote in his 11 March 1420 letter to Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, that Lithuanian and Samogitian are the same language.[37]  The use of Lithuanian continued at the Lithuanian royal court after the deaths of Vytautas the Great (1430) and Jogaila (1434).[34] For example, since the young Grand Duke Casimir IV Jagiellon was underage, the supreme control over the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was in the hands of the Lithuanian Council of Lords, presided by Jonas Goštautas, while Casimir IV Jagiellon was taught Lithuanian and customs of Lithuania by appointed court officials.[40][41][42][31] During the Polish szlachta's envoys visit to Casimir in 1446, they noticed that in Casimir's royal court the Lithuanian-speaking courtiers were mandatory, alongside the Polish courtiers.[28][43] Casimir IV Jagiellon's son Saint Casimir, who was subsequently announced as patron saint of Lithuania, was a polyglot and among other languages knew Lithuanian.[44] Grand Duke Alexander Jagiellon also could understand and speak Lithuanian as multiple Lithuanian priests served in his royal chapel and he also maintained a Lithuanian court.[28][45][46] In 1501, Erazm Ciołek, a priest of the Vilnius Cathedral, explained to the Pope that the Lithuanians preserve their language and ensure respect to it (Linguam propriam observant), but they also use the Ruthenian language for simplicity reasons because it is spoken by almost half of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.[28] A note written by Sigismund von Herberstein in the first half of the 16th century states that, in an ocean of Ruthenian in this part of Europe, there were two non-Ruthenian regions: Lithuania and Samogitia where its inhabitants spoke their own language, but many Ruthenians were also living among them.[47]  The earliest surviving written Lithuanian text is a translation dating from about 1503–1525 of the Lord's Prayer, the Hail Mary, and the Nicene Creed written in the Southern Aukštaitian dialect.[23] On 8 January 1547 the first Lithuanian book was printed – the Catechism of Martynas Mažvydas.[23] At the royal courts in Vilnius of Sigismund II Augustus, the last Grand Duke of Lithuania prior to the Union of Lublin, both Polish and Lithuanian were spoken equally widely.[34] In 1552 Sigismund II Augustus ordered that orders of the Magistrate of Vilnius be announced in Lithuanian, Polish, and Ruthenian.[48] The same requirement was valid for the Magistrate of Kaunas.[49][50] In the 16th century, following the decline of Ruthenian usage in favor of Polish in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Lithuanian language strengthened its positions in Lithuania due to reforms in religious matters and judicial reforms which allowed lower levels of the Lithuanian nobility to participate in the social-political life of the state.[28] In 1599, Mikalojus Daukša published his Postil and in its prefaces he expressed that the Lithuanian language situation had improved and thanked bishop Merkelis Giedraitis for his works.[28] The early 18th century was devastating for the Lithuanian speakers as the Great Northern War plague outbreak in 1700–1721 killed 49% of residents in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1/3 of residents in Lithuania proper and up to 1/2 of residents in Samogitia) and 53% of residents in Lithuania Minor (more than 90% of the deceased were Prussian Lithuanians).[51] On the other hand, Lithuanian language seminars were established in the University of Königsberg (1718) and in the Prussian University of Halle (1727).[52] Until 1741 in the Lithuanian Province (Provinz Litauen) of the Kingdom of Prussia, which encompassed the counties of Klaipėda, Tilsit, Ragnit, Insterburg, there were 275 Lithuanian primary schools (in multinational areas separate classes were formed for Lithuanian and German speakers), in 1800 – 411 Lithuanian schools.[52] In 1776–1790 about 1,000 copies of the first Catholic primer in Lithuanian – Mokslas skaitymo rašto lietuviško – were issued annually, and it continued to be published until 1864. Over 15,000 copies appeared in total.[53][54][55] The Constitution of 3 May 1791 was translated into the Lithuanian language shortly after its adoption by the Great Sejm.[56] During the Kościuszko Uprising (1794) directive documents were distributed and appeals were published in various languages, including Lithuanian, also the Lithuanian language was used for sermons dedicated to the uprising (e.g. preached at Church of St. Johns, Vilnius and other churches, as well as in military units).[57][58][59][60][61]  In 1864, following the January Uprising, Mikhail Muravyov, the Russian Governor General of Lithuania, banned the language in education and publishing and barred use of the Latin alphabet altogether, although books continued to be printed in Lithuanian across the border in East Prussia and in the United States.[62][63] Brought into the country by book smugglers (Lithuanian: knygnešiai) despite the threat of long prison sentences, they helped fuel growing nationalist sentiment that finally led to the lifting of the ban in 1904.[62][63] According to the Russian Empire Census of 1897 (at the height of the Lithuanian press ban), 53.5% of Lithuanians (10 years and older) were literate, while the average of the Russian Empire was only 24–27.7% (in the European part of Russia the average was 30%, in Poland – 40.7%).[54][64] In the Russian Empire Lithuanian children were mostly educated by their parents or in secret schools by "daractors" in native Lithuanian language, while only 6.9% attended Russian state schools due to resistance to Russification.[65][66][67] Russian governorates with significant Lithuanian populations had one of the highest population literacy rates: Vilna Governorate (in 1897 ~23.6–50% Lithuanian of whom 37% were literate), Kovno Governorate (in 1897 66% Lithuanian of whom 55.3% were literate), Suwałki Governorate (in 1897 in counties of the governorate where Lithuanian population was dominant 76,6% of males and 50,2% of females were literate).[68][69][70][71] In 1872, the German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck started Germanisation policies (Allgemeine Bestimmungen) after finishing the unification of Germany and the Lithuanian language education in primary schools of Lithuania Minor was started to be replaced with German, however due to parents protests the Lithuanian language education remained alongside German until the late 19th century.[52][72] Area (marked in greenish-yellow) where Lithuanian language was dominant in 1827, depicted in a map by Lithuania-born historian, geographer Stanisław Plater (1827) Area where Lithuanian language was dominantly spoken, including its islands and mixed territories in the late 19th century by Polish linguist Jan Michał Rozwadowski (1930) Ethnolinguistic area of Lithuanians and the Lithuanian language in 1917 by Prussian Lithuanian professor Vilius Gaigalaitis (Wilhelm Gaigalat), the dashed areas represent linguistically mixed border areas where Lithuanians formed a large minority Jonas Jablonskis (1860–1930) made significant contributions to the formation of standard Lithuanian.[73] The conventions of written Lithuanian had been evolving during the 19th century, but Jablonskis, in the introduction to his Lietuviškos kalbos gramatika, was the first to formulate and expound the essential principles that were so indispensable to its later development.[73][74] His proposal for Standard Lithuanian was based on his native Western Aukštaitian dialect with some features of the eastern Prussian Lithuanians' dialect spoken in Lithuania Minor.[73][74] These dialects[clarification needed] had preserved archaic phonetics mostly intact due to the influence of the neighbouring Old Prussian, while other dialects had experienced different phonetic shifts.  Lithuanian became the official language of the country following the restoration of Lithuania's statehood in 1918. The 1922 Constitution of Lithuania (the first permanent Lithuanian constitution) recognized it as the sole official language of the state and mandated its use throughout the state.[75][76] The improvement of education system during the interwar period resulted in 92% of literacy rate of the population in Lithuania in 1939 (those still illiterate were mostly elderly).[65] Following the Żeligowski's Mutiny in 1920, Vilnius Region was detached from Lithuania and was eventually annexed by Poland in 1922. This resulted in repressions of Lithuanians and mass-closure of Lithuanian language schools in the Vilnius Region, especially when Vilnius Voivode Ludwik Bociański issued a secret memorandum of 11 February 1936 which stated the measures for suppressing the Lithuanians in the region.[77][78][79][80] Some Lithuanian historians, like Antanas Tyla and Ereminas Gintautas, consider these Polish policies as amounting to an "ethnocide of Lithuanians".[77][78] Between 1862 and 1944, the Lithuanian schools were completely banned in Lithuania Minor and the language was almost completely eliminated there.[74] The Baltic-origin place names retained their basis for centuries in Prussia but were Germanized (e.g. Tilžė – Tilsit, Labguva – Labiau, Vėluva – Wehliau, etc.); however, after the annexation of the Königsberg region into the Russian SFSR, they were changed completely, regardless of previous tradition (e.g. Tilsit – Sovetsk, Labiau – Polesk, Wehliau – Znamensk, etc.).[81] The Soviet occupation of Lithuania in 1940, German occupation in 1941, and eventually Soviet re-occupation in 1944, reduced the independent Republic of Lithuania to the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic within the Soviet Union.[74] Soviet authorities introduced Lithuanian–Russian bilingualism,[74] and Russian, as the de facto official language of the USSR, took precedence and the use of Lithuanian was reduced in a process of Russification.[82][74] Many Russian-speaking workers and teachers migrated to the Lithuanian SSR (fueled by the industrialization in the Soviet Union).[83] Russian consequently came into use in state institutions: the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Lithuania (there were 80% Russians among the 22,000 Communist Party members in the Lithuanian SSR in 1948), radio and television (61–74% of broadcasts were in Russian in 1970).[83] Lithuanians passively resisted Russification and continued to use their own language.[84] On 18 November 1988, the Supreme Soviet of the Lithuanian SSR restored Lithuanian as the official language of Lithuania, under from the popular pro-independence movement Sąjūdis.[75] On 11 March 1990, the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania was passed. Lithuanian was recognized as sole official language of Lithuania in the Provisional Basic Law (Lithuanian: Laikinasis Pagrindinis Įstatymas) and the Constitution of 1992, written during the Lithuanian constitutional referendum.[75][85] Classification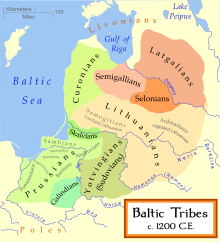  Lithuanian is one of two living Baltic languages, along with Latvian, and they constitute the eastern branch of the Baltic languages family.[86] An earlier Baltic language, Old Prussian, was extinct by the 18th century; the other Western Baltic languages, Curonian and Sudovian, became extinct earlier. Some theories, such as that of Jānis Endzelīns, considered that the Baltic languages form their own distinct branch of the family of Indo-European languages, and Endzelīns thought that the similarity between Baltic and Slavic was explicable through language contact.[87] There is also an opinion that suggests the union of Baltic and Slavic languages into a distinct sub-family of Balto-Slavic languages amongst the Indo-European family of languages. Such an opinion was first represented by August Schleicher.[88] Some supporters of the Baltic and Slavic languages unity even claim that Proto-Baltic branch did not exist, suggesting that Proto-Balto-Slavic split into three language groups: East Baltic, West Baltic and Proto-Slavic.[89][90][91][92] Antoine Meillet and Jan Baudouin de Courtenay, on the contrary, believed that the similarity between the Slavic and Baltic languages was caused by independent parallel development, and the Proto-Balto-Slavic language did not exist.[93]  An attempt to reconcile the opposing stances was made by Jan Michał Rozwadowski.[88] He proposed that the two language groups were indeed a unity after the division of Indo-European, but also suggested that after the two had divided into separate entities (Baltic and Slavic), they had posterior contact.[88] The genetic kinship view is augmented by the fact that Proto-Balto-Slavic is easily reconstructible with important proofs in historic prosody. The alleged (or certain, as certain as historical linguistics can be) similarities due to contact are seen in such phenomena as the existence of definite adjectives formed by the addition of an inflected pronoun (descended from the same Proto-Indo-European pronoun), which exist in both Baltic and Slavic yet nowhere else in the Indo-European family (languages such as Albanian and the Germanic languages developed definite adjectives independently), and that is not reconstructible for Proto-Balto-Slavic, meaning that they most probably developed through language contact.[94] The Baltic hydronyms area stretches from the Vistula River in the west to the east of Moscow and from the Baltic Sea in the north to the south of Kyiv.[95][96] Vladimir Toporov and Oleg Trubachyov (1961, 1962) studied Baltic hydronyms in Russian and Ukrainian territory.[97] Hydronyms and archaeology analysis show that the Slavs started migrating to the Baltic areas east and north-east directions in the 6–7th centuries, before then, the Baltic and Slavic boundary was south of the Pripyat River.[98] In the 1960s, Vladimir Toporov and Vyacheslav Ivanov made the following conclusions about the relationship between the Baltic and Slavic languages:
These scholars' theses do not contradict the Baltic and Slavic languages closeness and from a historical perspective, specify the Baltic-Slavic languages' evolution.[99][100] So, there are at least six points of view on the relationships between the Baltic and Slavic. However, as for the hypotheses related to the "Balto-Slavic problem", it is noted that they are more focused on personal theoretical constructions and deviate to some extent from the comparative method.[101] Geographic distributionLithuanian is spoken mainly in Lithuania. It is also spoken by ethnic Lithuanians living in today's Belarus, Latvia, Poland, and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, as well as by sizable emigrant communities in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Iceland, Ireland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, the United States, Uruguay, and Spain.[102] 2,955,200 people in Lithuania (including 3,460 Tatars), or about 86% of the 2015 population, are native Lithuanian speakers; most Lithuanian inhabitants of other nationalities also speak Lithuanian to some extent. The total worldwide Lithuanian-speaking population is about 3,200,000. Official statusLithuanian is the state language of Lithuania and an official language of the European Union.[75][103] Dialects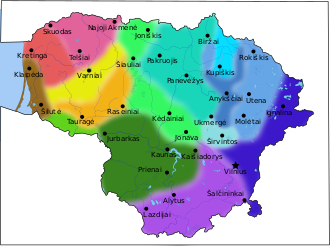 In the Compendium Grammaticae Lithvanicae, published in 1673, three dialects of Lithuanian are distinguished: Samogitian dialect (Latin: Samogitiae) of Samogitia, Royal Lithuania (Latin: Lithvaniae Regalis) and Ducal Lithuania (Latin: Lithvaniae Ducalis).[105] Ducal Lithuanian is described as pure (Latin: Pura), half-Samogitian (Latin: SemiSamogitizans) and having elements of Curonian (Latin: Curonizans).[105] Authors of the Compendium Grammaticae Lithvanicae singled out that the Lithuanians of the Vilnius Region (Latin: in tractu Vilnensi) tend to speak harshly, almost like Austrians, Bavarians and others speak German in Germany.[105] Due to the historical circumstances of Lithuania, Lithuanian-speaking territory was divided into Lithuania proper and Lithuania Minor, therefore, in the 16th–17th centuries, three regional variants of the common language emerged.[74][23] Lithuanians in Lithuania Minor spoke Western Aukštaitian dialect with specifics of Įsrutis and Ragainė environs (e.g. works of Martynas Mažvydas, Jonas Bretkūnas, Jonas Rėza, and Daniel Klein's Grammatica Litvanica).[74][23] The other two regional variants of the common language were formed in Lithuania proper: middle, which was based on the specifics of the Duchy of Samogitia (e.g. works of Mikalojus Daukša, Merkelis Petkevičius, Steponas Jaugelis‑Telega, Samuelis Boguslavas Chylinskis, and Mikołaj Rej's Lithuanian postil), and eastern, based on the specifics of Eastern Aukštaitians, living in Vilnius and its region (e.g. works of Konstantinas Sirvydas, Jonas Jaknavičius, and Robert Bellarmine's catechism).[74][23] In Vilnius University, there are preserved texts written in the Lithuanian language of the Vilnius area, a dialect of Eastern Aukštaitian, which was spoken in a territory located south-eastwards from Vilnius: the sources are preserved in works of graduates from Stanislovas Rapolionis-based Lithuanian language schools, graduate Martynas Mažvydas and Rapalionis relative Abraomas Kulvietis.[106][107] The development of Lithuanian in Lithuania Minor, especially in the 18th century, was successful due to many publications and research.[74][23] In contrast, the development of Lithuanian in Lithuania proper was obstructed due to the Polonization of the Lithuanian nobility, especially in the 18th century, and it was being influenced by the Samogitian dialect.[74][23] The Lithuanian-speaking population was also dramatically decreased by the Great Northern War plague outbreak in 1700–1721 which killed 49% of residents in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1/3 of residents in Lithuania proper and up to 1/2 of residents in Samogitia) and 53% of residents in Lithuania Minor (more than 90% of the deceased were Prussian Lithuanians).[51] Since the 19th century to 1925 the amount of Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania Minor (excluding Klaipėda Region) decreased from 139,000 to 8,000 due to Germanisation and colonization.[108]  As a result of a decrease in the usage of spoken Lithuanian in the eastern part of Lithuania proper, in the 19th century, it was suggested to create a standardized Lithuanian based on the Samogitian dialect.[74] Nevertheless, it was not accomplished because everyone offered their Samogitian subdialects and the Eastern and Western Aukštaitians offered their Aukštaitian subdialects.[74]  In the second half of the 19th century, when the Lithuanian National Revival intensified, and the preparations to publish a Lithuanian periodical press were taking place, the mostly south-western Aukštaitian revival writers did not use the 19th-century Lithuanian of Lithuania Minor as it was largely Germanized.[74] Instead, they used a more pure Lithuanian language which has been described by August Schleicher and Friedrich Kurschat and this way the written language of Lithuania Minor was transferred to resurgent Lithuania.[74] The most famous standardizer of the Lithuanian, Jonas Jablonskis, established the south-western Aukštaitian dialect, including the Eastern dialect of Lithuania Minor, as the basis of standardized Lithuanian in the 20th century, which led to him being nicknamed the father of standardized Lithuanian.[74][73] According to Polish professor Jan Otrębski's article published in 1931, the Polish dialect in the Vilnius Region and in the northeastern areas in general are very interesting variant of the Polish language as this dialect developed in a foreign territory which was mostly inhabited by the Lithuanians who were Belarusized (mostly) or Polonized, and to prove this Otrębski provided examples of Lithuanianisms in the Tutejszy language.[109][110] In 2015, Polish linguist Mirosław Jankowiak attested that many of the Vilnius Region's inhabitants who declare Polish nationality speak a Belarusian dialect which they call mowa prosta ('simple speech').[111] Currently, Lithuanian is divided into two dialects: Aukštaitian (Highland Lithuanian), and Samogitian (Lowland Lithuanian).[112][113] There are significant differences between standard Lithuanian and Samogitian and these are often described as separate languages.[112] The modern Samogitian dialect formed in the 13th–16th centuries under the influence of Curonian.[114] Lithuanian dialects are closely connected with ethnographical regions of Lithuania.[115] Even nowadays Aukštaitians and Samogitians can have considerable difficulties understanding each other if they speak with their dialects and not standard Lithuanian, which is mandatory to learn in the Lithuanian education system.[116] Dialects are divided into subdialects. Both dialects have three subdialects. Samogitian is divided into West, North and South; Aukštaitian into West (Suvalkiečiai), South (Dzūkian) and East.[117] ScriptLithuanian uses the Latin script supplemented with diacritics. It has 32 letters. In the collation order, y follows immediately after į (called i nosinė), because both y and į represent the same long vowel [iː]:[118]
In addition, the following digraphs are used, but are treated as sequences of two letters for collation purposes. The digraph ch represents a single sound, the velar fricative [x], while dz and dž are pronounced like straightforward combinations of their component letters (sounds): Dz dz [dz] (dzė), Dž dž [dʒ] (džė), Ch ch [x] (cha). The distinctive Lithuanian letter Ė was used for the first time in the Daniel Klein's Grammatica Litvanica and firmly established itself in Lithuanian since then.[119][120][121][122] However, linguist August Schleicher used Ë (with two points above it) instead of Ė for expressing the same.[123] In the Grammatica Litvanica Klein also established the letter W for marking the sound [v], the use of which was later abolished in Lithuanian (it was replaced with V, notably by authors of the Varpas newspaper).[119][123][124] The usage of V instead of W especially increased since the early 20th century, likely considerably influenced by Lithuanian press and schools.[124] The Lithuanian writing system is largely phonemic, i.e., one letter usually corresponds to a single phoneme (sound). There are a few exceptions: for example, the letter i represents either the vowel [ɪ], as in English sit, or is silent and merely indicates that the preceding consonant is palatalized. The latter is largely the case when i occurs after a consonant and is followed by a back or a central vowel, except in some borrowed words (e.g., the first consonant in lūpa [ˈɫûːpɐ], "lip", is a velarized dental lateral approximant; on the other hand, the first consonant in liūtas [ˈlʲuːt̪ɐs̪], "lion", is a palatalized alveolar lateral approximant; both consonants are followed by the same vowel, the long [uː], and no [ɪ] can be pronounced in liūtas). Title pages of two Lithuanian primers: Moksłas skaytima raszta lietuwiszka (1783 edition) and Mažas lietuviškas elementorius (1905 edition), demonstrating changes of Lithuanian orthography in the 19th–20th centuries Due to Polish influence, the Lithuanian alphabet included sz, cz and the Polish Ł for the first sound and regular L (without a following i) for the second: łupa, lutas.[121] During the Lithuanian National Revival in the 19th century the Polish Ł was abolished, while digraphs sz, cz (that are also common in the Polish orthography) were replaced with š and č from the Czech orthography because formally they were shorter.[121][123][125] Nevertheless, another argument to abolish sz and cz was to distinguish Lithuanian from Polish.[123] The new letters š and č were cautiously used in publications intended for more educated readers (e.g. Varpas, Tėvynės sargas, Ūkininkas), however sz and cz continued to be in use in publications intended for less educated readers as they caused tension in society and prevailed only after 1906.[126][127] The Lithuanians also adopted the letter ž from the Czechs.[121] The nasal vowels ą and ę were taken from the Polish spelling and began to be used by Renaissance Lithuanian writers, later the Lithuanians introduced the nasal vowels į and ų as analogues.[121][123] The letter ū is the latest addition by linguist Jonas Jablonskis.[128][123] A macron (on u), an ogonek (on a, e, i, and u), a dot (on e), and y (in place of i) are used for grammatical and historical reasons and always denote vowel length in Modern Standard Lithuanian. Acute, grave, and tilde diacritics are used to indicate pitch accents. However, these pitch accents are generally not written, except in dictionaries, grammars, and where needed for clarity, such as to differentiate homonyms and dialectal use. PhonologyConsonants
All Lithuanian consonants except /j/ have two variants: one non-palatalized and one palatalized, for example, /b/ – /bʲ/, /d/ – /dʲ/, /ɡ/ – /ɡʲ/ (see the chart above for the full consonant set, represented by IPA symbols). The consonants /f/, /x/, /ɣ/ and their palatalized counterparts are only found in loanwords. /t͡ɕ, d͡ʑ, ɕ, ʑ/ have been traditionally transcribed with ⟨t͡ʃʲ, d͡ʒʲ, ʃʲ, ʒʲ⟩, but they can be seen as equivalent transcriptions, with the former set being somewhat easier to write.[130] Vowels Lithuanian has six long vowels and four short ones (not including disputed phonemes marked in brackets). Length has traditionally been considered the distinctive feature, though short vowels are also more centralized and long vowels more peripheral:
DiphthongsLithuanian is traditionally described as having nine diphthongs, ai, au, ei, eu, oi, ou, ui, ie, and uo. However, some approaches (i.e., Schmalstieg 1982) treat them as vowel sequences rather than diphthongs; indeed, the longer component depends on the type of stress, whereas in diphthongs, the longer segment is fixed.
Pitch accentThe Lithuanian prosodic system is characterized by free accent and distinctive quantity (i.e. syllable weight). The word prosody of Lithuanian is sometimes described as a restricted tone system, also called a pitch accent system.[133] In Lithuanian, lexical words contain a single syllable that is prominent or stressed. Among those, heavy syllables – that is, those containing a long vowel, diphthong, or a sonorant coda – bear either one of two tones: a falling (or acute tone) or a rising (or circumflex tone). Light syllables (syllables with short vowels and optionally also obstruent codas) do not have the two-way contrast of heavy syllables. Grammar   The first prescriptive printed grammar of Lithuanian – Grammatica Litvanica was commissioned by the Duke of Prussia, Friedrich Wilhelm, for use in the Lithuanian-speaking parishes of East Prussia. It was written by Daniel Klein in Latin and was published by Johann Reusner in 1653 in Königsberg, Duchy of Prussia.[134][135][136] In ~1643 Christophorus Sapphun wrote the Lithuanian grammar Compendium Grammaticae Lithvanicae slightly earlier than Klein, however the edited variant of Sapphun's grammar was published only in 1673 by Theophylus Gottlieb Schultz.[137][138][139] In one of the first Lithuanian grammars – Compendium Grammaticae Lithvanicae, published in 1673, most of the given examples are with Lithuanian endings (e.g. names Jonas = Jonas, Jonuttis = Jonutis, etc.), therefore it allows to highlight the tendency of spelling the endings of words in the Old Lithuanian writings.[140] The Universitas lingvarum Litvaniae, published in Vilnius in 1737, is the oldest surviving grammar of Lithuanian published in the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.[141][142] The first scientific Compendium of Lithuanian was published in German in 1856/57 by August Schleicher, a professor at Charles University in Prague.[143][144] In it he describes Prussian-Lithuanian, which later became the "skeleton" (Būga) of modern Lithuanian. Schleicher asserted that Lithuanian can compete with the Greek and Roman (Old Latin) languages in perfection of forms.[145] Lithuanian is a highly inflected language. In Lithuanian, there are two grammatical genders for nouns (masculine and feminine) and three genders for adjectives, pronouns, numerals and participles (masculine, feminine and neuter). Every attribute must agree with the gender and number of the noun. The neuter forms of other parts of speech are used with a subject of an undefined gender (a pronoun, an infinitive etc.). There are twelve noun and five adjective declensions and one (masculine and feminine) participle declension.[146] Nouns and other parts of nominal morphology are declined in seven cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, instrumental, locative (inessive), and vocative. In older Lithuanian texts, three additional varieties of the locative case are found: illative, adessive and allative. The most common are the illative, which is still used, mostly in spoken language, and the allative, which survives in the standard language in some idiomatic usages. The adessive is nearly extinct. These additional cases are probably due to the influence of Uralic languages, with which Baltic languages have had a longstanding contact. (Uralic languages possess a great variety of noun cases, a number of which are specialised locative cases.) Lithuanian verbal morphology shows a number of innovations; namely, the loss of synthetic passive (which is hypothesized based on other archaic Indo-European languages, such as Greek and Latin), synthetic perfect (formed by means of reduplication) and aorist; forming subjunctive and imperative with the use of suffixes plus flexions as opposed to solely flections in, e.g., Ancient Greek; loss of the optative mood; merging and disappearing of the -t- and -nt- markers for the third-person singular and plural, respectively (this, however, occurs in Latvian and Old Prussian as well and may indicate a collective feature of all Baltic languages). On the other hand, Lithuanian verbal morphology retains a number of archaic features absent from most modern Indo-European languages (but shared with Latvian). This includes the synthetic form of the future tense with the help of the -s- suffix and three principal verbal forms with the present tense stem employing the -n- and -st- infixes. There are three verbal conjugations. The verb būti is the only auxiliary verb in the language. Together with participles, it is used to form dozens of compound forms. In the active voice, each verb can be inflected for any of the following moods:
In the indicative mood and indirect moods, all verbs can have eleven tenses:
The indirect mood, used only in written narrative speech, has the same tenses corresponding to the appropriate active participle in nominative case; e.g., the past of the indirect mood would be nešęs, while the past iterative inchoative of the indirect mood would be būdavęs benešąs. Since it is a nominal form, this mood cannot be conjugated but must match the subject's number and gender. The subjunctive (or conditional) and the imperative moods have three tenses. Subjunctive: present (neščiau), past (būčiau nešęs), inchoative (būčiau benešąs); imperative: present (nešk), perfect (būk nešęs) and inchoative (būk benešąs). The infinitive has only one form (nešti). These forms, except the infinitive and indirect mood, are conjugative, having two singular, two plural persons, and the third person form common both for plural and singular. In the passive voice, the form number is not as rich as in the active voice. There are two types of passive voice in Lithuanian: present participle (type I) and past participle (type II) (in the examples below types I and II are separated with a slash). They both have the same moods and tenses:
Lithuanian has the richest participle system of all Indo-European languages, having participles derived from all simple tenses with distinct active and passive forms, and two gerund forms. In practical terms, the rich overall inflectional system makes the word order have a different meaning than in more analytic languages such as English. The English phrase "a car is coming" translates as "atvažiuoja automobilis" (the theme first), while "the car is coming" – "automobilis atvažiuoja" (the theme first; word order inversion). Lithuanian also has a very rich word derivation system and an array of diminutive suffixes. Today there are two definitive books on Lithuanian grammar: one in English, the Introduction to Modern Lithuanian (called Beginner's Lithuanian in its newer editions) by Leonardas Dambriūnas, Antanas Klimas and William R. Schmalstieg; and another in Russian, Vytautas Ambrazas' Грамматика литовского языка (Lithuanian Grammar). Another recent book on Lithuanian grammar is the second edition of Review of Modern Lithuanian Grammar by Edmund Remys, published by Lithuanian Research and Studies Center, Chicago, 2003. Vocabulary  Indo-European vocabularyLithuanian retains cognates to many words found in classical languages, such as Sanskrit and Latin. These words are descended from Proto-Indo-European. A few examples are the following:
This even extends to grammar, where for example Latin noun declensions ending in -um often correspond to Lithuanian -ų, with the Latin and Lithuanian fourth declensions being particularly close. Many of the words from this list are similar to other Indo-European languages, including English and Russian. The contribution of Lithuanian was influential in the reconstruction of Proto-Indo-European. Lexical and grammatical similarities between Baltic and Slavic languages suggest an affinity between these two language groups. On the other hand, there exist a number of Baltic (particularly Lithuanian) words without counterparts in Slavic languages, but which are similar to words in Sanskrit or Latin. The history of the relationship between Baltic and Slavic languages, and our understanding of the affinity between the two groups, remain in dispute (see: Balto-Slavic languages). LoanwordsIn a 1934 book entitled Die Germanismen des Litauischen. Teil I: Die deutschen Lehnwörter im Litauischen, K. Alminauskis found 2,770 loanwords, of which about 130 were of uncertain origin. The majority of the loanwords were found to have been derived from Polish, Belarusian, and German, with some evidence that these languages all acquired the words from contacts and trade with Prussia during the era of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.[147] Loanwords comprised about 20% of the vocabulary used in the first book printed in Lithuanian in 1547, Martynas Mažvydas's Catechism.[148] But as a result of language preservation and purging policies, Slavic loanwords currently constitute only 1.5% of the Standard Lithuanian lexicon, while German loanwords constitute only 0.5% of it.[149] The majority of loanwords in the 20th century arrived from Russian.[150] Towards the end of the 20th century, a number of words and expressions related to new technologies and telecommunications were borrowed from English. The Lithuanian government has an established language policy that encourages the development of equivalent vocabulary to replace loanwords.[151] However, despite the government's best efforts to avoid the use of loanwords in Lithuanian, many English words have become accepted and are now included in Lithuanian language dictionaries.[152][153] In particular, words having to do with new technologies have permeated the Lithuanian vernacular, including such words as:
Other common foreign words have also been adopted by Lithuanian. Some of these include: These words have been modified to suit the grammatical and phonetic requirements of Lithuanian, mostly by adding -as ending, but their foreign roots are obvious. Old LithuanianThe earliest known Lithuanian glosses (~1520–1530) written in the margins of Johannes Herolt's book Liber Discipuli de eruditione Christifidelium. Left: word ßch[ÿ]kſtu[m]aſ (parsimony); Right: words teprÿdav[ſ]ʒÿ (let it strike) and vbagÿſte (indigence).      The language of the earliest Lithuanian writings, in the 16th and 17th centuries, is known as Old Lithuanian and differs in some significant respects from the Lithuanian of today. Besides the specific differences given below, nouns, verbs, and adjectives still had separate endings for the dual number. The dual persists today in some dialects. Example:
PronunciationThe vowels written ą, ę, į, ų were still pronounced as long nasal vowels,[154] not as long oral vowels as in today's Lithuanian. The original Baltic long ā was still retained as such, e.g. bralis 'brother' (modern brólis). NounsCompared to modern Lithuanian, there were three additional cases. The original locative case had been replaced by four so-called postpositive cases, the inessive case, illative case, adessive case and allative case, which correspond to the prepositions "in", "into", "at" and "towards", respectively. They were formed by affixing a postposition to one of the previous cases:
The inessive has become the modern locative case, while the other three have disappeared. Note, however, that the illative case is still used occasionally in the colloquial language (mostly in the singular): Lietuvon 'to Lithuania', miestan 'to the city'. This form is relatively productive: for instance, it is not uncommon to hear "skrendame Niujorkan (we are flying to New York)". There are some words still used in adessive case: esu "namie" (could be equally substituted with "namuose") I'm 'at home'. The uncontracted dative plural -mus was still common. AdjectivesAdjectives could belong to all four accent classes in Old Lithuanian (now they can only belong to classes 3 and 4). Additional remnants of i-stem adjectives still existed, e.g.:
Additional remnants of u-stem adjectives still existed, e.g. rūgštùs 'sour':
No u-stem remnants existed in the dative singular and locative plural. Definite adjectives, originally involving a pronoun suffixed to an adjective, had not merged into a single word in Old Lithuanian. Examples:
VerbsThe Proto-Indo-European class of athematic verbs still existed in Old Lithuanian:
The optative mood (i.e. the third-person imperative) still had its own endings, -ai for third-conjugation verbs and -ie for other verbs, instead of using regular third-person present endings. SyntaxWord order was freer in Old Lithuanian. For example, a noun in the genitive case could either precede or follow the noun it modifies. Further reading
See alsoCitations
General sources
External links Lithuanian edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Wikivoyage has a phrasebook for Lithuanian. For a list of words relating to Lithuanian language, see the Lithuanian language category of words in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||