|
Machining  Machining is a manufacturing process where a desired shape or part is created using the controlled removal of material, most often metal, from a larger piece of raw material by cutting. Machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing,[1] which utilizes machine tools, in contrast to additive manufacturing (e.g. 3D printing), which uses controlled addition of material. Machining is a major process of the manufacture of many metal products, but it can also be used on other materials such as wood, plastic, ceramic, and composites.[2] A person who specializes in machining is called a machinist. As a commercial venture, machining is generally performed in a machine shop, which consists of one or more workrooms containing primary machine tools. Although a machine shop can be a standalone operation, many businesses maintain internal machine shops or tool rooms that support their specialized needs. Much modern-day machining uses computer numerical control (CNC), in which computers control the movement and operation of mills, lathes, and other cutting machines. History and terminologyThe precise meaning of the term machining has changed over the past one and a half centuries as technology has advanced in a number of ways. In the 18th century, the word machinist meant a person who built or repaired machines. This person's work was primarily done by hand, using processes such as the carving of wood and the writing-forging and hand-filing of metal. At the time, millwrights and builders of new kinds of engines (meaning, more or less, machines of any kind), such as James Watt or John Wilkinson, would fit the definition. The noun machine tool and the verb to machine (machined, machining) did not yet exist.[citation needed] Around the middle of the 20th century, the latter words were coined as the concepts they described evolved into widespread existence. Therefore, during the Machine Age, machining referred to (what we today might call) the "traditional" machining processes, such as turning, boring, drilling, milling, broaching, sawing, shaping, planing, abrasive cutting, reaming, and tapping.[3] In these "traditional" or "conventional" machining processes, machine tools, such as lathes, milling machines, drill presses, or others, are used with a sharp cutting tool to remove material to achieve a desired geometry.[4] Since the advent of new technologies in the post–World War II era, such as electrical discharge machining, electrochemical machining, electron beam machining, photochemical machining, and ultrasonic machining, the retronym "conventional machining" can be used to differentiate those classic technologies from the newer ones. Currently, "machining" without qualification usually implies the traditional machining processes. In the decades of the 2000s and 2010s, as additive manufacturing (AM) evolved beyond its earlier laboratory and rapid prototyping contexts and began to become standard throughout all phases of manufacturing, the term subtractive manufacturing became common retronymously in logical contrast with AM, covering essentially any removal processes also previously covered by the term machining. The two terms are effectively synonymous, although the long-established usage of the term machining continues. This is comparable to the idea that the verb sense of contact evolved because of the proliferation of ways to contact someone (telephone, email, IM, SMS, and so on) but did not entirely replace the earlier terms such as call, talk to, or write to.[citation needed]  Machining operationsMachining is any process in which a cutting tool removes material from the workpiece (the workpiece is often called the "work"). Relative motion is required in traditional machining between the device and the work to remove material; non-traditional machining processes use other methods of material removal, such as electric current in EDM (electro-discharge machining). This relative motion is achieved in most machining operations by moving (by lateral rotary or lateral motion) either the tool, or the workpiece. The shape of the tool, the relative motion, and its penetration into the work, produce the desired shape of the resulting work surface. Machining operations can be broken down into traditional, and non-traditional operations. Within the traditional operations, there are two categories of machining based on the shape they machine; being circular shapes that includes; turning, boring, drilling, reaming, threading and more, and various/straight shapes that includes; milling, broaching, sawing, grinding and shaping.  Cutting toolA cutting tool has one or more sharp cutting edges and is made of a harder material than the work material. The cutting edge serves to separate the chip from the parent work material. Connected to the cutting edge are the two surfaces of the tool:
The rake face, which directs the flow of the newly formed chip, is oriented at a certain angle and is called the rake angle "α." It is measured relative to the plane perpendicular to the work surface. The rake angle can be positive or negative. The flank of the tool provides a clearance between the tool and the newly formed work surface, thus protecting the surface from abrasion, which would degrade the finish. This angle between the work and flank surfaces is called the relief angle. There are two basic types of cutting tools:
A single-point tool has one cutting edge for turning, boring, and planing. During machining, the device's point penetrates below the work part's original work surface. The fact is sometimes rounded to a certain radius, called the nose radius. Multiple cutting-edge tools have more than one cutting edge and usually achieve their motion relative to the work part by rotating. Drilling and milling use turning multiple-cutting-edge tools. Although the shapes of these tools are different from a single-point device, many elements of tool geometry are similar.  Traditional machiningCircular machining operations
Various shape machining
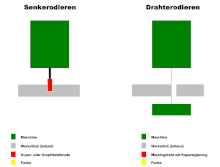 Non-traditional machining
An unfinished workpiece requiring machining must have some material cut away to create a finished product. A finished product would be a workpiece that meets the specifications set out for that workpiece by engineering drawings or blueprints. For example, a workpiece may require a specific outside diameter. A lathe is a machine tool that can create that diameter by rotating a metal workpiece so that a cutting tool can cut metal away, creating a smooth, round surface matching the required diameter and surface finish. A drill can remove the metal in the shape of a cylindrical hole. Other tools that may be used for metal removal are milling machines, saws, and grinding machines. Many of these same techniques are used in woodworking. Machining requires attention to many details for a workpiece to meet the specifications in the engineering drawings or blueprints. Besides the obvious problems related to correct dimensions, there is the problem of achieving the right finish or surface smoothness on the workpiece. The inferior finish found on the machined surface of a workpiece may be caused by incorrect clamping, a dull tool, or inappropriate presentation of a device. Frequently, this poor surface finish, known as chatter, is evident by an undulating or regular finish of waves on the machined surfaces of the workpiece. Cutting conditions Relative motion is required between the tool and work to perform a machining operation. The primary action is at a specific cutting speed. In addition, the device must be moved laterally across the work. This is a much slower motion called the feed. The remaining dimension of the cut is the penetration of the cutting tool below the original work surface, reaching the cut's depth. Speed, feed, and depth of cut are called the cutting conditions.[6] They form the three dimensions of the machining process, and for certain operations, their product can be used to obtain the material removal rate for the process: where
Stages in metal cuttingMachining operations usually divide into two categories, distinguished by purpose and cutting conditions:
Roughing cuts are used to remove a large amount of material from the starting work part as rapidly as possible, i.e., with a significant Material Removal Rate (MRR), to produce a shape close to the desired form but leaving some material on the piece for a subsequent finishing operation. Finishing cuts complete the part and achieve the final dimension, tolerances, and surface finish. In production machining jobs, one or more roughing cuts are usually performed on the work, followed by one or two finishing cuts. Roughing operations are done at high feeds and depths – feeds of 0.4–1.25 mm/rev (0.015–0.050 in/rev) and depths of 2.5–20 mm (0.100–0.750 in) are typical, but actual values depend on the workpiece materials. Finishing operations are carried out at low feeds and depths – dinners of 0.0125–0.04 mm/rev (0.0005–0.0015 in/rev) and depths of 0.75–2.0 mm (0.030–0.075 in) are typical.[citation needed] Cutting speeds are lower in roughing than in finishing. A cutting fluid is often applied to the machining operation to cool and lubricate the cutting tool. Determining whether a cutting fluid should be used and, if so, choosing the proper cutting fluid is usually included within the scope of the cutting condition. Today other forms of metal cutting are becoming increasingly popular. An example of this is water jet cutting. Water jet cutting involves pressurized water over 620 MPa (90 000 psi) and can cut metal and have a finished product. This process is called cold cutting, which eliminates the damage caused by a heat-affected zone, as opposed to laser and plasma cutting. Relationship of subtractive and additive techniquesWith the recent proliferation of additive manufacturing technologies, conventional machining has been retronymously classified, in thought and language, as a subtractive manufacturing method. In narrow contexts, additive and subtractive methods may compete with each other. In the broad context of entire industries, their relationship is complementary. Each method has its advantages over the other. While additive manufacturing methods can produce very intricate prototype designs impossible to replicate by machining, strength and material selection may be limited.[7] See also
References
Bibliography
Further reading
External links
|




