|
N-Methylformamide
N-Methylformamide (NMF) is a colorless, nearly odorless, organic compound and secondary amide with molecular formula CH3NHCHO, which is a liquid at room temperature. NMF is mainly used as a reagent in various organic syntheses with limited applications as a highly polar solvent.[1] NMF is closely related to other formamides, notably formamide and dimethylformamide (DMF). However, industrial use and production of NMF are far less than for either of these other formamides. DMF is favored over NMF as a solvent due to its greater stability.[1] Annual production of NMF can be assumed to be significantly less than the production of either formamide (100,000 tons) or DMF (500,000 tons).[1] Structure and propertiesBecause of slow rotation about the N-C(O) bond, NMF exists as two rotamers that can be distinguished by NMR spectroscopy. The two principal resonance structures for one of these rotamers is shown: This description highlights the partial double bond that exists between the carbonyl carbon and nitrogen, which raises the rotational barrier. Thus, the molecule is not able to freely rotate around its main axis and the (E)-configuration is preferred due to steric repulsion of the larger substituents.[2] This molecule has been tentatively identified in interstellar space by the ALMA radio telescope. It may have formed on dust grains. This could prove to be a key molecule for interstellar pre-biotic chemistry due to its peptide bond.[3] PreparationNMF is typically prepared by allowing methylamine to react with methyl formate:[1]
A less common alternative to this process is transamidation involving formamide:[1]
UsesNMF is a specialized solvent in oil refineries. It is a precursor in specialized amidation reactions where formamide would not be suitable. These reactions can generally be categorized by the following equation:
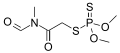 Laboratory usesNMF is the precursor to methyl isocyanide, a ligand in coordination chemistry.[4] NMF is used as a solvent in Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors. References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




