|
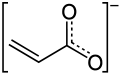
AcrylateAcrylates (IUPAC: prop-2-enoates) are the salts, esters, and conjugate bases of acrylic acid. The acrylate ion is the anion CH2=CHCO−2. Often, acrylate refers to esters of acrylic acid, the most common member being methyl acrylate. These acrylates contain vinyl groups. These compounds are of interest because they are bifunctional: the vinyl group is susceptible to polymerization and the carboxylate group carries myriad functionalities.[1] MonomersAcrylates are defined by the formula CH2=CHCO2R, where R can be many groups:
The versatility of the resulting polymers is owed to the range of R groups.
Acrylate derivativesMethacrylates ( CH2=C(CH3)CO2R) and cyanoacrylates ( CH2=C(CN)CO2R,) are closely related to acrylates. The feature a methyl and a nitrile in place of the H alpha to the carboxy functional group. They share several properties, being polymerized by radicals and being colorless.[2]
Polymers Some acrylate polymers (poly(methyl methacrylate) etc. not included): Acrylate monomers are used to form acrylate polymers. Most commonly, these polymers are in fact copolymers, being derived from two monomers.[3][4] Related polymers In the same way that several variants of acrylic esters are known, so too are the corresponding polymers. Their properties strongly depends on the substituent. A large family of acrylate-like polymers are derived from methyl methacrylate and many related esters, especially polymethyl methacrylate. A second large family of acrylate-like polymers are derived from ethyl cyanoacrylate, which gives rise to cyanoacrylates. Yet another family of acrylate-related polymers are the polyacrylamides, especially the parent derived from acrylamide. Other usesIn addition to forming polymers, acrylate esters participate in other reactions relevant to organic chemistry. They are Michael acceptors and dienophiles. They undergo transesterification. ProductionAcrylates are industrially prepared by treating acrylic acid with the corresponding alcohol in presence of a catalyst. The reaction with lower alcohols (methanol, ethanol) takes place at 100–120 °C with acidic heterogeneous catalysts (cation exchanger). The reaction of higher alcohols (n-butanol, 2-ethylhexanol) is catalysed with sulfuric acid in homogeneous phase. Acrylates of even higher alcohols are obtainable by transesterification of lower esters catalysed by titanium alcoholates or organic tin compounds (e.g. dibutyltin dilaurate).[5] See also
References
Information related to Acrylate |