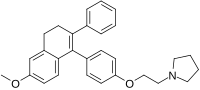
Chemical compound
Pharmaceutical compound
Nafoxidine Other names U-11,000A; NSC-70735 Routes of By mouth ATC code
1-[2-[4-(6-Methoxy-2-phenyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-yl)phenoxy]ethyl]pyrrolidine
CAS Number PubChem CID IUPHAR/BPS ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) ECHA InfoCard 100.222.756 Formula C 29 H 31 N O 2 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
COC1=CC2=C(C=C1)C(=C(CC2)C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OCCN5CCCC5
InChI=1S/C29H31NO2/c1-31-26-14-16-28-24(21-26)11-15-27(22-7-3-2-4-8-22)29(28)23-9-12-25(13-10-23)32-20-19-30-17-5-6-18-30/h2-4,7-10,12-14,16,21H,5-6,11,15,17-20H2,1H3
Key:JEYWNNAZDLFBFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Nafoxidine (INN Tooltip International Nonproprietary Name ; developmental code names U-11,000A ) or nafoxidine hydrochloride (USAN Tooltip United States Adopted Name ) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) or partial antiestrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was developed for the treatment of advanced breast cancer by Upjohn in the 1970s but was never marketed.[ 1] [ 2] [ 3] tamoxifen and clomifene , which are also triphenylethylene derivatives.[ 2] postcoital contraceptive , but was subsequently repurposed for the treatment of breast cancer.[ 4] [ 5] [ 6] side effects including ichthyosis , partial hair loss , and phototoxicity of the skin in almost all patients,[ 5] [ 4] [ 7]
Nafoxidine is a long-acting estrogen receptor ligand , with a nuclear retention in the range of 24 to 48 hours or more.[ 8]
References
^ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3 ^ a b Craig JV, Furr BJ (5 February 2010). Hormone Therapy in Breast and Prostate Cancer ISBN 978-1-59259-152-7 ^ Weber GF (22 July 2015). Molecular Therapies of Cancer ISBN 978-3-319-13278-5 ^ a b McDaniel RE, Maximov PY, Jordan VC (2013). "Estrogen-mediated mechanisms to control the growth and apoptosis of breast cancer cells: a translational research success story" . Vitamins and Hormones . 93 : 1–49. doi :10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00007-1 . PMID 23810002 . ^ a b Coelingh Bennink HJ, Verhoeven C, Dutman AE, Thijssen J (January 2017). "The use of high-dose estrogens for the treatment of breast cancer" . Maturitas . 95 : 11–23. doi :10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.10.010 PMID 27889048 . ^ Steinbaum FL, De Jager RL, Krakoff IH (1978). "Clinical trial of nafoxidine in advanced breast cancer". Medical and Pediatric Oncology . 4 (2): 123–126. doi :10.1002/mpo.2950040207 . PMID 661750 . ^ Lupulescu A (24 October 1990). Hormones and Vitamins in Cancer Treatment ISBN 978-0-8493-5973-6 ^ Hammond CB, Maxson WS (January 1982). "Current status of estrogen therapy for the menopause". Fertility and Sterility . 37 (1): 5–25. doi :10.1016/S0015-0282(16)45970-4 . PMID 6277697 . ^ Jensen EV, Jordan VC (June 2003). "The estrogen receptor: a model for molecular medicine" . Clin. Cancer Res . 9 (6): 1980–9. PMID 12796359 . ^ Howell A, Jordan VC (2013). "Adjuvant Antihormone Therapy". In Craig JV (ed.). Estrogen Action, Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators And Women's Health: Progress And Promise doi :10.1142/9781848169586_0010 . ISBN 978-1-84816-959-3
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor
Agonists
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol 2-Hydroxyestrone 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol 3α-Androstanediol 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Androstanediol 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Fluoroestradiol 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 4-Methoxyestradiol 4-Methoxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7α-Methylestradiol 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) 11β-Chloromethylestradiol 11β-Methoxyestradiol 15α-Hydroxyestradiol 16-Ketoestradiol 16-Ketoestrone 16α-Fluoroestradiol 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodoestradiol 16α-LE2 16β-Hydroxyestrone 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol )17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone (methandrostenolone) , nandrolone and esters , many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Cyclodiol Cyclotriol DHEA DHEA-S ent -EstradiolEpiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin ERA-63 (ORG-37663) Esterified estrogens Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estrogenic substances Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestriol Ethylestradiol Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Hexolame Hippulin Hydroxyestrone diacetate Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Norethisterone Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Prodiame Prolame Promestriene RU-16117 Quinestradol Quinestrol Tibolone Xenoestrogens: Anise -related (e.g., anethole , anol , dianethole , dianol , photoanethole )Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin , phloretin , phlorizin (phloridzin) , wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol , psoralidin )Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF , 8-prenylnaringenin , apigenin , baicalein , baicalin , biochanin A , calycosin , catechin , daidzein , daidzin , ECG , EGCG , epicatechin , equol , formononetin , glabrene , glabridin , genistein , genistin , glycitein , kaempferol , liquiritigenin , mirificin , myricetin , naringenin , penduletin , pinocembrin , prunetin , puerarin , quercetin , tectoridin , tectorigenin )Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., enterodiol , enterolactone , nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) )Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium )Pesticides (e.g., alternariol , dieldrin , endosulfan , fenarimol , HPTE , methiocarb , methoxychlor , triclocarban , triclosan )Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis ), diosgenin , guggulsterone )Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol , campesterol , stigmasterol )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone , α-zearalenol , β-zearalenol , zearalenone , zeranol (α-zearalanol) , taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Steroid -like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol , miroestrol )Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol , rhaponticin )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols , bisphenols (e.g., BPA , BPF , BPS ), DDT , parabens , PBBs , PHBA , phthalates , PCBs )Others (e.g., agnuside , rotundifuran ) MixedSERMs Tooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators ) Antagonists
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
GPER Tooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor
Agonists Antagonists Unknown