Chemical compound
Pharmaceutical compound
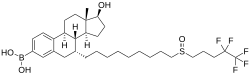
ZB716 Other names Fulvestrant-3-boronic acid; Fulvestrant-3-boronoate; 7α-[9-[(4,4,5,5,5-Pentafluoropentyl)-sulfinyl]nonyl]-3-(dihydroxy-boryl)estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17β-ol Routes of By mouth [ 1] Drug class Antiestrogen ; Selective estrogen receptor degrader
[(7R ,8R ,9S ,13S ,14S ,17S )-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-7-[9-(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentylsulfinyl)nonyl]-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a ]phenanthren-3-yl]boronic acid
CAS Number PubChem CID UNII Formula C 32 H 48 B F 5 O 4 S Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol ) Melting point 230 °C (446 °F) (decomposes)
B(C1=CC2=C(C=C1)[C@H]3CC[C@]4([C@H]([C@@H]3[C@@H](C2)CCCCCCCCCS(=O)CCCC(C(F)(F)F)(F)F)CC[C@@H]4O)C)(O)O
InChI=1S/C32H48BF5O4S/c1-30-17-15-26-25-12-11-24(33(40)41)21-23(25)20-22(29(26)27(30)13-14-28(30)39)10-7-5-3-2-4-6-8-18-43(42)19-9-16-31(34,35)32(36,37)38/h11-12,21-22,26-29,39-41H,2-10,13-20H2,1H3/t22-,26-,27+,28+,29-,30+,43?/m1/s1
Key:FIAYIYKWRBIBQG-GDWZZRAASA-N
ZB716 , also known as fulvestrant-3-boronic acid , is a synthetic , steroidal , orally active antiestrogen which is under development for the treatment of estrogen receptor (ER)-positive metastatic breast cancer .[ 1] silent antagonist of the ERα (IC50 = 4.1 nM) as well as a selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD).[ 1] analogue and prodrug of fulvestrant in which the C3 hydroxyl group has been replaced with a boronic acid moiety .[ 1] pharmacodynamic properties.[ 1] intramuscular injection , ZB716 is less susceptible to first-pass metabolism , and in relation to this, is orally active.[ 1]
A single oral dose of 8.3 mg/kg ZB716 to mice has been found to result in an over 160 ng/mL (160,000 pg/mL) maximal concentration of the drug in circulation, a level far in excess of the 15.2 ng/mL (15,200 pg/mL) concentration achieved with subcutaneous injection of fulvestrant in mice.[ 1] bioavailability compared to fulvestrant and hence may allow for greater systemic exposure and therapeutic benefit.[ 1]
ZB716 produces fulvestrant as an active metabolite in vivo [ 1] [ 1]
Clinical Development
As of December 2020, it is in a phase I clinical trial for ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer.[ 2]
See also
References
^ a b c d e f g h i j Liu J, Zheng S, Akerstrom VL, Yuan C, Ma Y, Zhong Q, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Guo S, Ma P, Skripnikova EV, Bratton MR, Pannuti A, Miele L, Wiese TE, Wang G (2016). "Fulvestrant-3 Boronic Acid (ZB716): An Orally Bioavailable Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulator (SERD)" . J. Med. Chem . 59 (17): 8134–40. doi :10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00753 . PMC 5499704 PMID 27529700 . ^ ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04669587
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor
Agonists
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol 2-Hydroxyestrone 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol 3α-Androstanediol 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Androstanediol 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Fluoroestradiol 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 4-Methoxyestradiol 4-Methoxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7α-Methylestradiol 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) 11β-Chloromethylestradiol 11β-Methoxyestradiol 15α-Hydroxyestradiol 16-Ketoestradiol 16-Ketoestrone 16α-Fluoroestradiol 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodoestradiol 16α-LE2 16β-Hydroxyestrone 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol )17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone (methandrostenolone) , nandrolone and esters , many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Cyclodiol Cyclotriol DHEA DHEA-S ent -EstradiolEpiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin ERA-63 (ORG-37663) Esterified estrogens Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estrogenic substances Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestriol Ethylestradiol Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Hexolame Hippulin Hydroxyestrone diacetate Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Norethisterone Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Prodiame Prolame Promestriene RU-16117 Quinestradol Quinestrol Tibolone Xenoestrogens: Anise -related (e.g., anethole , anol , dianethole , dianol , photoanethole )Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin , phloretin , phlorizin (phloridzin) , wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol , psoralidin )Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF , 8-prenylnaringenin , apigenin , baicalein , baicalin , biochanin A , calycosin , catechin , daidzein , daidzin , ECG , EGCG , epicatechin , equol , formononetin , glabrene , glabridin , genistein , genistin , glycitein , kaempferol , liquiritigenin , mirificin , myricetin , naringenin , penduletin , pinocembrin , prunetin , puerarin , quercetin , tectoridin , tectorigenin )Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., enterodiol , enterolactone , nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) )Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium )Pesticides (e.g., alternariol , dieldrin , endosulfan , fenarimol , HPTE , methiocarb , methoxychlor , triclocarban , triclosan )Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis ), diosgenin , guggulsterone )Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol , campesterol , stigmasterol )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone , α-zearalenol , β-zearalenol , zearalenone , zeranol (α-zearalanol) , taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Steroid -like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol , miroestrol )Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol , rhaponticin )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols , bisphenols (e.g., BPA , BPF , BPS ), DDT , parabens , PBBs , PHBA , phthalates , PCBs )Others (e.g., agnuside , rotundifuran ) MixedSERMs Tooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators ) Antagonists
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
GPER Tooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor
Agonists Antagonists Unknown