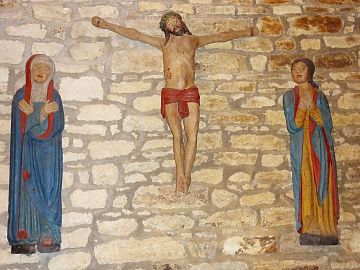|
Plougastel-Daoulas
Plougastel-Daoulas (French pronunciation: [pluɡastɛl daulas]; Breton: Plougastell-Daoulaz) is a commune in the Finistère department, located in the administrative region of Brittany, northwestern France. PopulationInhabitants of Plougastel-Daoulas are called plougastels in French.
Breton languageThe municipality launched a linguistic plan concerning the Breton language through Ya d'ar brezhoneg on 28 October 2005. In 2008, 18.98% of primary-school children attended bilingual schools.[5] StrawberriesThe region is famous for its production of strawberries (gariguette de Plougastel). The New World species of strawberry, Fragaria chiloensis, which had been introduced into France by Amédée-François Frézier (1682–1773), flourished in the marine climate of Plougastel. Gardeners there had observed that this species bore abundant fruit when Fragaria moschata and Fragaria virginiana were planted in alternating rows with it. There had been failed attempts to cultivate fragaria chiloensis in Anjou, Touraine, and the lower-Loire areas. TourismThe Albert Louppe Bridge or Plougastel Bridge over the Elorn River is within the commune. International relationsPlougastel is twinned with Westport, County Mayo, a town in the west of Ireland, and also with Saltash, a town in the south-east of Cornwall, United Kingdom. Paintings depicting Plougastel-Daoulas
Churches and chapels in Plougastel-DaoulasÉglise Saint-PierreThe parish church was damaged during the bombing of the 22 and 23 August 1944 and subsequently rebuilt. It contains a notable "rosary" altarpiece and a "mise au Tombeau" both from the old church.[6]
Chapelle Saint-AdrienThis chapel has an interesting 17th-century sculpture in wood entitled "Saint Martin et le Pauvre". It depicts Saint Martin's charitable works. See old postcard above showing the sculpture.[7][8] The chapelle Saint-Adrien dates to 1549 according to the inscription over the south porch. The chapel contains many statues of saints.[6]
Chapelle Saint-JeanDating to the 15th century, enlarged in 1607 and restored in 1780. This chapel is associated with a pardon known as the "Pardon des Oiseaux". Chapelle Saint-GuénoléDedicated to the founder of the abbey at Landévennec, the chapel was restored in 1896. A beam in the chapel bears the date 1514 and by the chevet window there is a stone inscribed "M. I. Le Galle. Cariou. v. 1706". The altarpiece dates to the 17th century and was restored in 1993. There is a statue in polychromed wood of Saint Guénolé in the chapel to the left side of the altarpiece.[6] There are two triptychs in the chapel. One is the Saint Caradec triptych and the other is the Saint Louis triptych.
Chapelle Notre-Dame-de-la-Fontaine-BlancheThis was once the priory of the abbey of Daoulas. The clock tower dates to 1702. There are three altars in the chapel dedicated to Saint Lawrence, Saint Mary Magdalene and the Virgin Mary ("Notre-Dame"). These were consecrated in 1508 by Jean Davesnes.[6] Chapelle Saint-ClaudeDates to the 16th century. The date 1652 is inscribed above the main entrance. A statue of saint-Claude on a throne is placed by the altarpiece by the main altar. Other dates inscribed are "H. et D. Le Maucaire prieur recteur de Plougastel Jan Corre Fabrique 1661" on the west façade, "Jehan Le Gall Fabrique 1661" on the gable of the south wing and in the sacristy "1747". A painting by Yves Hen in the chapel dates to 1661.[6]
Other calvariesOf the many calvaries around Plougastel-Daoulas, two involve the sculptor Roland Doré (sculptor).
The mystery of PlougastelNot far from nearby Anse du Caro, a message is carved on a rock, beginning with "grocar drear diozeevbio", followed on by other writings in an unknown language. The text includes enigmatic drawings, such as a heart linked to a cross, and a sailboat close to the sea. Two numbers on the rock are decryptable: 1786 and 1787.[9] See also
References
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Plougastel-Daoulas.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||