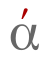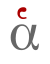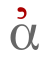|
Greek diacritics
Greek orthography has used a variety of diacritics starting in the Hellenistic period. The more complex polytonic orthography (Greek: πολυτονικό σύστημα γραφής, romanized: polytonikó sýstīma grafī́s), which includes five diacritics, notates Ancient Greek phonology. The simpler monotonic orthography (Greek: μονοτονικό σύστημα γραφής, romanized: monotonikó sýstīma grafī́s), introduced in 1982, corresponds to Modern Greek phonology, and requires only two diacritics. Polytonic orthography (from Ancient Greek πολύς (polýs) 'much, many' and τόνος (tónos) 'accent') is the standard system for Ancient Greek and Medieval Greek and includes:
Since in Modern Greek the pitch accent has been replaced by a dynamic accent (stress), and /h/ was lost, most polytonic diacritics have no phonetic significance, and merely reveal the underlying Ancient Greek etymology. Monotonic orthography (from Ancient Greek μόνος (mónos) 'single' and τόνος (tónos) 'accent') is the standard system for Modern Greek. It retains two diacritics:
A tonos and a diaeresis can be combined on a single vowel to indicate a stressed vowel after a hiatus, as in the verb ταΐζω (/taˈizo/, "I feed"). Although it is not a diacritic, the hypodiastole (comma) has in a similar way the function of a sound-changing diacritic in a handful of Greek words, principally distinguishing ό,τι (ó,ti, "whatever") from ότι (óti, "that").[1] History The original Greek alphabet did not have diacritics. The Greek alphabet is attested since the 8th century BC, and until 403 BC, variations of the Greek alphabet—which exclusively used what are now known as capitals—were used in different cities and areas. From 403 on, the Athenians decided to employ a version of the Ionian alphabet. With the spread of Koine Greek, a continuation of the Attic dialect, the Ionic alphabet superseded the other alphabets, known as epichoric, with varying degrees of speed. The Ionian alphabet, however, also consisted only of capitals. Introduction of breathings The rough and smooth breathings were introduced in classical times in order to represent the presence or absence of an /h/ in Attic Greek, which had adopted a form of the alphabet in which the letter ⟨Η⟩ (eta) was no longer available for this purpose as it was used to represent the long vowel /ɛː/. Introduction of accentsDuring the Hellenistic period (3rd century BC), Aristophanes of Byzantium introduced the breathings—marks of aspiration (the aspiration however being already noted on certain inscriptions, not by means of diacritics but by regular letters or modified letters)—and the accents, of which the use started to spread, to become standard in the Middle Ages. It was not until the 2nd century AD that accents and breathings appeared sporadically in papyri. The need for the diacritics arose from the gradual divergence between spelling and pronunciation. Uncial scriptThe majuscule, i.e., a system where text is written entirely in capital letters, was used until the 8th century, when the minuscule polytonic supplanted it. Grave accent ruleBy the Byzantine period, the modern rule that turns an acute accent (oxeia) on the last syllable into a grave accent (bareia)—except before a punctuation sign or an enclitic—had been firmly established. Certain authors have argued that the grave originally denoted the absence of accent; the modern rule is, in their view, a purely orthographic convention. Originally, certain proclitic words lost their accent before another word and received the grave, and later this was generalized to all words in the orthography. Others—drawing on, for instance, evidence from ancient Greek music—consider that the grave was "linguistically real" and expressed a word-final modification of the acute pitch.[2][3][4] Stress accentIn the later development of the language, the ancient pitch accent was replaced by an intensity or stress accent, making the three types of accent identical, and the /h/ sound became silent. SimplificationAt the beginning of the 20th century (official since the 1960s), the grave was replaced by the acute, and the iota subscript and the breathings on the rho were abolished, except in printed texts.[5] Greek typewriters from that era did not have keys for the grave accent or the iota subscript, and these diacritics were also not taught in primary schools where instruction was in Demotic Greek. Official adoption of monotonic systemFollowing the official adoption of the demotic form of the language, the monotonic orthography was imposed by law in 1982. The latter uses only the acute accent (or sometimes a vertical bar, intentionally distinct from any of the traditional accents) and diaeresis and omits the breathings. This simplification has been criticized on the grounds that polytonic orthography provides a cultural link to the past.[6][7] Modern use of polytonic systemSome individuals, institutions, and publishers continue to prefer the polytonic system (with or without grave accent), though an official reintroduction of the polytonic system does not seem probable. The Greek Orthodox church, the daily newspaper Estia, as well as books written in Katharevousa continue to use the polytonic orthography. Though the polytonic system was not used in Classical Greece, these critics argue that modern Greek, as a continuation of Byzantine and post-medieval Greek, should continue their writing conventions. Some textbooks of Ancient Greek for foreigners have retained the breathings, but dropped all the accents in order to simplify the task for the learner.[8] DescriptionPolytonic Greek uses many different diacritics in several categories. At the time of Ancient Greek, each of these marked a significant distinction in pronunciation. Monotonic orthography for Modern Greek uses only two diacritics, the tonos and diaeresis (sometimes used in combination) that have significance in pronunciation, similar to vowels in Spanish. Initial /h/ is no longer pronounced, and so the rough and smooth breathings are no longer necessary. The unique pitch patterns of the three accents have disappeared, and only a stress accent remains. The iota subscript was a diacritic invented to mark an etymological vowel that was no longer pronounced, so it was dispensed with as well.
The transliteration of Greek names follows Latin transliteration of Ancient Greek; modern transliteration is different, and does not distinguish many letters and digraphs that have merged by iotacism. Accents
The accents (Ancient Greek: τόνοι, romanized: tónoi, singular: τόνος, tónos) are placed on an accented vowel or on the last of the two vowels of a diphthong (ά, but αί) and indicated pitch patterns in Ancient Greek. The precise nature of the patterns is not certain, but the general nature of each is known. The acute accent (ὀξεῖα, oxeîa, 'sharp' or "high") – 'ά' – marked high pitch on a short vowel or rising pitch on a long vowel. The acute is also used on the first of two (or occasionally three) successive vowels in Modern Greek to indicate that they are pronounced together as a stressed diphthong. The grave accent (βαρεῖα, bareîa, 'heavy' or "low", modern varia) – 'ὰ' – marked normal or low pitch. The grave was originally written on all unaccented syllables.[9] By the Byzantine period it was only used to replace the acute at the end of a word if another accented word follows immediately without punctuation. The circumflex (περισπωμένη, perispōménē, 'twisted around') – 'ᾶ' – marked high and falling pitch within one syllable. In distinction to the angled Latin circumflex, the Greek circumflex is printed in the form of either a tilde (◌̃) or an inverted breve (◌̑). It was also known as ὀξύβαρυς oxýbarys "high-low" or "acute-grave", and its original form (^ ) was from a combining of the acute and grave diacritics. Because of its compound nature, it only appeared on long vowels or diphthongs. Breathings
The breathings were written over a vowel or ρ. The rough breathing (Ancient Greek: δασὺ πνεῦμα, romanized: dasù pneûma; Latin spīritus asper)—'ἁ'—indicates a voiceless glottal fricative (/h/) before the vowel in Ancient Greek. In Greek grammar, this is known as aspiration. This is different from aspiration in phonetics, which applies to consonants, not vowels.
The smooth breathing (ψιλὸν πνεῦμα, psīlòn pneûma; Latin spīritus lēnis)—'ἀ'—marked the absence of /h/. A double rho in the middle of a word was originally written with smooth breathing on the first rho and rough breathing on the second one (διάῤῥοια). In Latin, this was transcribed as rrh (diarrhoea or diarrhea). Coronis The coronis (κορωνίς, korōnís, 'curved') marks a vowel contracted by crasis. It was formerly an apostrophe placed after the contracted vowel, but is now placed over the vowel and is identical to the smooth breathing. Unlike the smooth breathing, it often occurs inside a word. Subscript
The iota subscript (ὑπογεγραμμένη, hypogegramménē, 'written under')—'ι'—is placed under the long vowels ᾱ, η, and ω to mark the ancient long diphthongs ᾱι, ηι, and ωι, in which the ι is no longer pronounced. AdscriptNext to a capital, the iota subscript is usually written as a lower-case letter (Αι), in which case it is called iota adscript (προσγεγραμμένη, prosgegramménē, 'written next to'). DiaeresisIn Ancient Greek, the diaeresis (Greek: διαίρεσις or διαλυτικά, dialytiká, 'distinguishing') – ϊ – appears on the letters ι and υ to show that a pair of vowel letters is pronounced separately, rather than as a diphthong or as a digraph for a simple vowel. In Modern Greek, the diaeresis usually indicates that two successive vowels are pronounced separately (as in κοροϊδεύω /ko.ro.iˈðe.vo/, "I trick, mock"), but occasionally, it marks vowels that are pronounced together as an unstressed diphthong rather than as a digraph (as in μποϊκοτάρω /boj.koˈtar.o/, "I boycott"). The distinction between two separate vowels and an unstressed diphthong is not always clear, although two separate vowels are far more common. The diaeresis can be combined with the acute, grave and circumflex but never with breathings, since the letter with the diaeresis cannot be the first vowel of the word.[10] In Modern Greek, the combination of the acute and diaeresis indicates a stressed vowel after a hiatus. Vowel lengthIn textbooks and dictionaries of Ancient Greek, the macron—'ᾱ'—and breve—'ᾰ'—are often used over α, ι, and υ to indicate that it is long or short, respectively. Nonstandard diacriticsCaronIn some modern non-standard orthographies of Greek dialects, such as Cypriot Greek, Griko, and Tsakonian, a caron (ˇ) may be used on some consonants to show a palatalized pronunciation.[11][12] They are not encoded as precombined characters in Unicode, so they are typed by adding the U+030C ◌̌ COMBINING CARON to the Greek letter. Latin diacritics on Greek letters may not be supported by many fonts, and as a fall-back a caron may be replaced by an iota ⟨ι⟩ following the consonant. An example of a Greek letter with a combining caron and its pronunciation: τ̌ /c/. Dot aboveA dot diacritic was used above some consonants and vowels in Karamanli Turkish, which was written with the Greek alphabet.[13] Position in lettersDiacritics are written above lower-case letters and at the upper left of capital letters. In the case of a digraph, the second vowel takes the diacritics. A breathing diacritic is written to the left of an acute or grave accent but below a circumflex. Accents are written above a diaeresis or between its two dots. In uppercase (all-caps), accents and breathings are eliminated, in titlecase they appear to the left of the letter rather than above it. Unlike other diacritics, the dieresis is kept above letters also in uppercase. Different conventions exist for the handling of the iota subscript. Diacritics can be found above capital letters in medieval texts and in the French typographical tradition up to the 19th century. [14] Example
Computer encodingThere have been problems in representing polytonic Greek on computers, and in displaying polytonic Greek on computer screens and printouts, but these have largely been overcome by the advent of Unicode and appropriate fonts. IETF language tagThe IETF language tags have registered subtag codes for the different orthographies:[15]
UnicodeWhile the tónos of monotonic orthography looks similar to the oxeîa of polytonic orthography in most typefaces, Unicode has historically separate symbols for letters with these diacritics. For example, the monotonic "Greek small letter alpha with tónos" is at U+03AC, while the polytonic "Greek small letter alpha with oxeîa" is at U+1F71. The monotonic and polytonic accent however have been de jure equivalent since 1986, and accordingly the oxeîa diacritic in Unicode decomposes canonically to the monotonic tónos—both are underlyingly treated as equivalent to the multiscript acute accent, U+0301, since letters with oxia decompose to letters with tonos, which decompose in turn to base letter plus multiscript acute accent. Thus:
Where a distinction needs to be made (in historic textual analysis, for example), the existence of individual code points and a suitable distinguishing typeface (computer font) make this possible. Upper case
Lower case
See also
References
Further reading
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Greek diacritics. General information:
Polytonic Greek fonts:
How-to guides for polytonic keyboard layouts:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||